Identification of Listeria monocytogenes in vivo-induced genes by fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- PMID: 11447181
- PMCID: PMC98595
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.8.5016-5024.2001
Identification of Listeria monocytogenes in vivo-induced genes by fluorescence-activated cell sorting
Abstract
Listeria monocytogenes is a gram-positive, intracellular, food-borne pathogen capable of causing severe infections in immunocompromised or pregnant individuals, as well as numerous animal species. Genetic analysis of Listeria pathogenesis has identified several genes which are crucial for virulence. The transcription of most of these genes has been shown to be induced upon entry of Listeria into the host cell. To identify additional genes that are induced in vivo and may be required for L. monocytogenes pathogenesis, a fluorescence-activated cell-sorting technique was initiated. Random fragments of the L. monocytogenes chromosome were cloned into a plasmid carrying a promoterless green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene, and the plasmids were transformed into the L. monocytogenes actA mutant DP-L1942. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) was used to isolate L. monocytogenes clones that exhibited increased GFP expression within macrophage-like J774 cells but had relatively low levels of GFP expression when the bacteria were extracellular. Using this strategy, several genes were identified, including actA, that exhibited such an expression profile. In-frame deletions of two of these genes, one encoding the putative L. monocytogenes uracil DNA glycosylase (ung) and one encoding a protein with homology to the Bacillus subtilis YhdP hemolysin-like protein, were constructed and introduced into the chromosome of wild-type L. monocytogenes 10403s. The L. monocytogenes 10403s ung deletion mutant was not attenuated for virulence in mice, while the yhdP mutant exhibited a three- to sevenfold reduction in virulence.
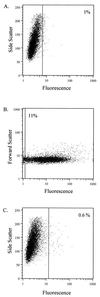
Figures





Similar articles
-
Differential expression of Listeria monocytogenes virulence genes in mammalian host cells.Mol Gen Genet. 1999 Mar;261(2):323-36. doi: 10.1007/pl00008633. Mol Gen Genet. 1999. PMID: 10102368
-
Characterization of the groESL operon in Listeria monocytogenes: utilization of two reporter systems (gfp and hly) for evaluating in vivo expression.Infect Immun. 2001 Jun;69(6):3924-32. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.6.3924-3932.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11349060 Free PMC article.
-
VirR, a response regulator critical for Listeria monocytogenes virulence.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Sep;57(5):1367-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04776.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16102006
-
Classes and functions of Listeria monocytogenes surface proteins.Pol J Microbiol. 2004;53(2):75-88. Pol J Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15478352 Review.
-
The sophisticated survival strategies of the pathogen Listeria monocytogenes.Int Microbiol. 1998 Mar;1(1):11-8. Int Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 10943336 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of genes induced in Listeria monocytogenes during growth and attachment to cut cabbage, using differential display.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Sep;71(9):5236-43. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.9.5236-5243.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16151109 Free PMC article.
-
Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae gene expression induced in vivo in a chinchilla model of otitis media.Infect Immun. 2003 Jun;71(6):3454-62. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.6.3454-3462.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12761130 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of fumarate hydratase from Rickettsia prowazekii, the agent of typhus and suspected relative of the mitochondria.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011 Sep 1;67(Pt 9):1123-8. doi: 10.1107/S174430911102690X. Epub 2011 Aug 16. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011. PMID: 21904061 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale quantitative analysis of sources of variation in the actin polymerization-based movement of Listeria monocytogenes.Biophys J. 2005 Jul;89(1):703-23. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.051219. Epub 2005 May 6. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 15879472 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular gene expression profile of Listeria monocytogenes.Infect Immun. 2006 Feb;74(2):1323-38. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.2.1323-1338.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16428782 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barker L P, Brooks D M, Small P L. The identification of Mycobacterium marinumgenes differentially expressed in macrophage phagosomes using promoter fusions to green fluorescent protein. Mol Microbiol. 1998;29:1167–1177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

