4-Hydroxytamoxifen binds to and deactivates the estrogen-related receptor gamma
- PMID: 11447273
- PMCID: PMC37529
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.151244398
4-Hydroxytamoxifen binds to and deactivates the estrogen-related receptor gamma
Abstract
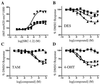
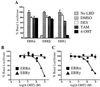
The estrogen-related receptors (ERR alpha, ERR beta, and ERR gamma) form a family of orphan nuclear receptors that share significant amino acid identity with the estrogen receptors, but for which physiologic roles remain largely unknown. By using a peptide sensor assay, we have identified the stilbenes diethylstilbestrol (DES), tamoxifen (TAM), and 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) as high-affinity ligands for ERR gamma. In direct binding assays, 4-OHT had a K(d) value of 35 nM, and both DES and TAM displaced radiolabeled 4-OHT with K(i) values of 870 nM. In cell-based assays, 4-OHT binding caused a dissociation of the complex between ERR gamma and the steroid receptor coactivator-1, and led to an inhibition of the constitutive transcriptional activity of ERR gamma. ERR alpha did not bind 4-OHT, but replacing a single amino acid predicted to be in the ERR alpha ligand-binding pocket with the corresponding ERR gamma residue allowed high-affinity 4-OHT binding. These results demonstrate the existence of high-affinity ligands for the ERR family of orphan receptors, and identify 4-OHT as a molecule that can regulate the transcriptional activity of ERR gamma.
Figures
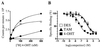

References
-
- Freedman L P. Cell. 1999;97:5–8. - PubMed
-
- Heery D M, Kalkhoven E, Hoare S, Parker M G. Nature (London) 1997;387:733–736. - PubMed
-
- Makishima M, Okamoto A Y, Repa J J, Tu H, Learned R M, Luk A, Hull M V, Lustig K D, Mangelsdorf D J, Shan B. Science. 1999;284:1362–1365. - PubMed
-
- Xu L, Glass C K, Rosenfeld M G. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1999;9:140–147. - PubMed
-
- Willson T M, Brown P J, Sternbach D D, Henke B R. J Med Chem. 2000;43:527–550. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

