Deficiency of human BRCA2 leads to impaired homologous recombination but maintains normal nonhomologous end joining
- PMID: 11447276
- PMCID: PMC37489
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.151253498
Deficiency of human BRCA2 leads to impaired homologous recombination but maintains normal nonhomologous end joining
Abstract
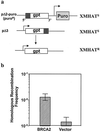
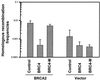
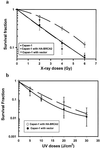
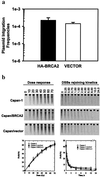
Carriers of BRCA2 germline mutations are at high risk to develop early-onset breast cancer. The underlying mechanisms of how BRCA2 inactivation predisposes to malignant transformation have not been established. Here, we provide direct functional evidence that human BRCA2 promotes homologous recombination (HR), which comprises one major pathway of DNA double-strand break repair. We found that up-regulated HR after transfection of wild-type (wt) BRCA2 into a human tumor line with mutant BRCA2 was linked to increased radioresistance. In addition, BRCA2-mediated enhancement of HR depended on the interaction with Rad51. In contrast to the tumor suppressor BRCA1, which is involved in multiple DNA repair pathways, BRCA2 status had no impact on the other principal double-strand break repair pathway, nonhomologous end joining. Thus, there exists a specific regulation of HR by BRCA2, which may function to maintain genomic integrity and suppress tumor development in proliferating cells.
Figures
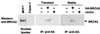
Similar articles
-
Nonhomologous end-joining of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-stranded breaks in human tumor cells deficient in BRCA1 or BRCA2.Cancer Res. 2001 Jan 1;61(1):270-7. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11196174
-
BRCA1 regulates RAD51 function in response to DNA damage and suppresses spontaneous sister chromatid replication slippage: implications for sister chromatid cohesion, genome stability, and carcinogenesis.Cancer Res. 2005 Dec 15;65(24):11384-91. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2156. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16357146
-
Strand invasion involving short tract gene conversion is specifically suppressed in BRCA2-deficient hamster cells.Oncogene. 2004 Dec 2;23(56):9136-41. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208178. Oncogene. 2004. PMID: 15480413
-
Lessons learned from BRCA1 and BRCA2.Oncogene. 2000 Dec 11;19(53):6159-75. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203968. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 11156530 Review.
-
The breast cancer susceptibility gene, BRCA2: at the crossroads between DNA replication and recombination?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000 Feb 29;355(1394):191-8. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2000.0558. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000. PMID: 10724455 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic features of renal cell carcinoma with venous tumor thrombus.Sci Rep. 2018 May 10;8(1):7477. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25544-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29748622 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation mediates early phase histone eviction at DNA lesions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Apr 6;48(6):3001-3013. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31965183 Free PMC article.
-
Sensitization of Pancreatic Cancers to Gemcitabine Chemoradiation by WEE1 Kinase Inhibition Depends on Homologous Recombination Repair.Neoplasia. 2015 Oct;17(10):757-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2015.09.006. Neoplasia. 2015. PMID: 26585231 Free PMC article.
-
Biallelic BRCA2 Mutations Shape the Somatic Mutational Landscape of Aggressive Prostate Tumors.Am J Hum Genet. 2016 May 5;98(5):818-829. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Am J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27087322 Free PMC article.
-
Heterozygous mutation in BRCA2 induces accelerated age-dependent decline in sperm quality with male subfertility in rats.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 2;15(1):447. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-84184-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39747609 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

