TrkB-like immunoreactivity is present on geniculocortical afferents in layer IV of kitten primary visual cortex
- PMID: 11447584
- PMCID: PMC2553095
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.1075
TrkB-like immunoreactivity is present on geniculocortical afferents in layer IV of kitten primary visual cortex
Abstract
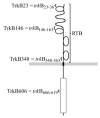
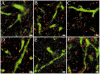
Exogenous administration of the neurotrophins brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) or neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5), or blockade of their endogenous actions, have been reported to affect the anatomic organization and physiological responses of neurons in developing mammalian primary visual cortex. Experimental alteration of levels of these neurotrophic factors can also influence the morphology of the geniculocortical afferents that project from the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) to primary visual cortex. BDNF and NT-4/5 are ligands of the TrkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Although multiple populations of cortical neurons express TrkB, it is not known whether geniculocortical afferents express this receptor on their axon branches in visual cortex. We have anatomically labeled geniculocortical afferents of postnatal day 40 kittens with the anterograde neuronal tracer Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L) and performed double-label immunofluorescence with a panel of anti-TrkB antibodies. Confocal microscopy and object-based colocalization analysis were used to measure levels of TrkB-like immunoreactivity (IR) on geniculocortical afferents in layer IV of primary visual cortex. By using a conservative analysis involving a comparison of measured colocalization with the amount of colocalization expected based on random overlap of TrkB puncta and PHA-L--labeled afferents, 3 of 5 anti-TrkB antibodies tested showed significant colocalization with the geniculocortical axons. Results for the other two antibodies were indeterminate. The indices obtained for colocalization of TrkB and geniculocortical afferents were also compared with the equivalent index obtained for GAD65, a protein that has a similar overall expression pattern to that of TrkB but is not expressed on geniculocortical axons. This analysis indicated that TrkB was present on geniculocortical axons for all five TrkB antibodies tested. TrkB-like IR was also observed on neuronal somata in the LGN. These results indicate that TrkB receptors on geniculocortical afferents are potential mediators of the actions of BDNF and NT-4/5 in developing visual cortex.
Copyright 2001 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Differential effects of cortical neurotrophic factors on development of lateral geniculate nucleus and superior colliculus neurons: anterograde and retrograde actions.Development. 2003 Feb;130(3):611-22. doi: 10.1242/dev.00224. Development. 2003. PMID: 12490566
-
Synaptic density in geniculocortical afferents remains constant after monocular deprivation in the cat.J Neurosci. 1999 Dec 15;19(24):10829-42. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-24-10829.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10594065 Free PMC article.
-
Morphology of single geniculocortical afferents and functional recovery of the visual cortex after reverse monocular deprivation in the kitten.J Neurosci. 1998 Dec 1;18(23):9896-909. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-23-09896.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9822746 Free PMC article.
-
Numerical relationships between geniculocortical afferents and pyramidal cell modules in cat primary visual cortex.Cereb Cortex. 1993 Jan-Feb;3(1):69-78. doi: 10.1093/cercor/3.1.69. Cereb Cortex. 1993. PMID: 8439740 Review.
-
A numerical analysis of the geniculocortical input to striate cortex in the monkey.Cereb Cortex. 1994 May-Jun;4(3):215-29. doi: 10.1093/cercor/4.3.215. Cereb Cortex. 1994. PMID: 8075528 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue sparing and functional recovery following experimental traumatic brain injury is provided by treatment with an anti-myelin-associated glycoprotein antibody.Eur J Neurosci. 2006 Dec;24(11):3063-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05197.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17156367 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-autonomous TrkB signaling in presynaptic retinal ganglion cells mediates axon arbor growth and synapse maturation during the establishment of retinotectal synaptic connectivity.J Neurosci. 2007 Mar 7;27(10):2444-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4434-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17344382 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophin NT-4/5 Promotes Structural Changes in Neurons of the Developing Visual Cortex.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Dec 22:2023.12.20.572693. doi: 10.1101/2023.12.20.572693. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 38187745 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Effects of optic nerve injury, glaucoma, and neuroprotection on the survival, structure, and function of ganglion cells in the mammalian retina.J Physiol. 2008 Sep 15;586(18):4393-400. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.156729. Epub 2008 Jun 19. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18565994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Low-intensity repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation improves abnormal visual cortical circuit topography and upregulates BDNF in mice.J Neurosci. 2014 Aug 6;34(32):10780-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0723-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25100609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonini A, Stryker MP. Rapid remodeling of axonal arbors in the visual cortex. Science. 1993b;260:1819–1821. - PubMed
-
- Aoki C, Wu K, Elste A, Len G-W, Lin S-Y, McAuliffe G, Black IB. Localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB receptors to postsynaptic densities of adult rat cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Res. 2000;59:454–463. - PubMed
-
- Barbacid M. The Trk family of neurotrophin receptors. J Neurobiol. 1994;25:1386–1403. - PubMed
-
- Bozzi Y, Borrelli E. Absence of the dopamine D2 receptor leads to a decreased expression of GDNF and NT-4 mRNAs in restricted brain areas. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:1275–1284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

