Large-scale chromatin decondensation and recondensation regulated by transcription from a natural promoter
- PMID: 11448988
- PMCID: PMC2196867
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200011069
Large-scale chromatin decondensation and recondensation regulated by transcription from a natural promoter
Abstract
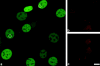
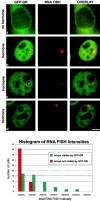
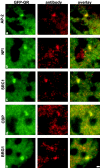
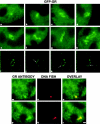
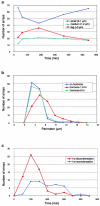
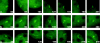
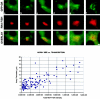
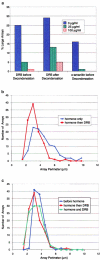
We have examined the relationship between transcription and chromatin structure using a tandem array of the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) promoter driving a ras reporter. The array was visualized as a distinctive fluorescent structure in live cells stably transformed with a green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged glucocorticoid receptor (GR), which localizes to the repeated MMTV elements after steroid hormone treatment. Also found at the array by immunofluorescence were two different steroid receptor coactivators (SRC1 and CBP) with acetyltransferase activity, a chromatin remodeler (BRG1), and two transcription factors (NFI and AP-2). Within 3 h after hormone addition, arrays visualized by GFP-GR or DNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) decondensed to varying degrees, in the most pronounced cases from a approximately 0.5-microm spot to form a fiber 1-10 microm long. Arrays later recondensed by 3-8 h of hormone treatment. The degree of decondensation was proportional to the amount of transcript produced by the array as detected by RNA FISH. Decondensation was blocked by two different drugs that inhibit polymerase II, 5,6-dichloro-1-beta-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole (DRB) and alpha-amanitin. These observations demonstrate a role for polymerase in producing and maintaining decondensed chromatin. They also support fiber-packing models of higher order structure and suggest that transcription from a natural promoter may occur at much higher DNA-packing densities than reported previously.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nuclear factor I-mediated repression of the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter is abrogated by the coactivators p300/CBP and SRC-1.J Biol Chem. 1999 Mar 12;274(11):7072-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.11.7072. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10066764
-
Chromatin remodeling complexes interact dynamically with a glucocorticoid receptor-regulated promoter.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Aug;19(8):3308-22. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-02-0123. Epub 2008 May 28. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18508913 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell analysis of glucocorticoid receptor action reveals that stochastic post-chromatin association mechanisms regulate ligand-specific transcription.Mol Endocrinol. 2006 Nov;20(11):2641-55. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0091. Epub 2006 Jul 27. Mol Endocrinol. 2006. PMID: 16873444
-
Steroid hormone receptor status defines the MMTV promoter chromatin structure in vivo.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1995 Jun;53(1-6):421-9. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00088-h. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1995. PMID: 7626491 Review.
-
Transcriptional control by steroid hormones: the role of chromatin.Ciba Found Symp. 1995;191:7-17; discussion 17-23. doi: 10.1002/9780470514757.ch2. Ciba Found Symp. 1995. PMID: 8582206 Review.
Cited by
-
Large-scale chromatin organization: the good, the surprising, and the still perplexing.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;26:69-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.10.002. Epub 2013 Nov 13. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24529248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53-dependent chromatin relaxation is required for DNA double-strand break repair.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025 Feb 25;57(5):701-711. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2025008. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2025. PMID: 40007254 Free PMC article.
-
The spatial dynamics of tissue-specific promoters during C. elegans development.Genes Dev. 2010 Apr 15;24(8):766-82. doi: 10.1101/gad.559610. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 20395364 Free PMC article.
-
The active FMR1 promoter is associated with a large domain of altered chromatin conformation with embedded local histone modifications.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 15;103(33):12463-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605343103. Epub 2006 Aug 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16891414 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1-induced large-scale chromatin unfolding and allele-specific effects of cancer-predisposing mutations.J Cell Biol. 2001 Dec 10;155(6):911-21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200108049. Epub 2001 Dec 10. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11739404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersson, K., R. Mahr, B. Bjorkroth, and B. Daneholt. 1982. Rapid reformation of the thick chromosome fiber upon completion of RNA synthesis at the Balbiani ring genes in Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma. 87:33–48. - PubMed
-
- Archer, T.K., P. Lefebvre, R.G. Wolford, and G.L. Hager. 1992. Transcription factor loading on the MMTV promoter: a bimodal mechanism for promoter activation. Science. 255:1573–1576. - PubMed
-
- Archer T.K., H.L. Lee, M.G. Cordingley, J.S. Mymryk, G. Fragoso, D.S. Berard, and G.L. Hager. 1994. Differential steroid hormone induction of transcription from the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol. Endocrinol. 8:568–576. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner, M. 1990. Puffs, genes, and hormones revisited. Cell. 61:1–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

