Functional analysis of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors of Arabidopsis
- PMID: 11449057
- PMCID: PMC139548
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.010087
Functional analysis of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors of Arabidopsis
Abstract
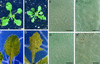
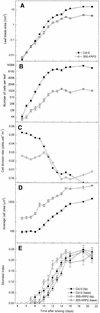
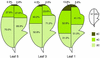
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors, such as the mammalian p27(Kip1) protein, regulate correct cell cycle progression and the integration of developmental signals with the core cell cycle machinery. These inhibitors have been described in plants, but their function remains unresolved. We have isolated seven genes from Arabidopsis that encode proteins with distant sequence homology with p27(Kip1), designated Kip-related proteins (KRPs). The KRPs were characterized by their domain organization and transcript profiles. With the exception of KRP5, all presented the same cyclin-dependent kinase binding specificity. When overproduced, KRP2 dramatically inhibited cell cycle progression in leaf primordia cells without affecting the temporal pattern of cell division and differentiation. Mature transgenic leaves were serrated and consisted of enlarged cells. Although the ploidy levels in young leaves were unaffected, endoreduplication was suppressed in older leaves. We conclude that KRP2 exerts a plant growth inhibitory activity by reducing cell proliferation in leaves, but, in contrast to its mammalian counterparts, it may not control the timing of cell cycle exit and differentiation.
Figures

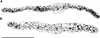
References
-
- Beeckman, T., and Viane, R. (2000). Embedding thin plant specimens for oriented sectioning. Biotech. Histochem. 75, 23–26. - PubMed
-
- Bell, M.H., Halford, N.G., Ormrod, J.C., and Francis, D. (1993). Tobacco plants transformed with cdc25, a mitotic inducer gene from fission yeast. Plant Mol. Biol. 23, 445–451. - PubMed
-
- Burssens, S., de Almeida Engler, J., Beeckman, T., Richard, C., Shaul, O., Ferreira, P., Van Montagu, M., and Inzé, D. (2000). Developmental expression of the Arabidopsis thaliana CycA2;1 gene. Planta 211, 623–631. - PubMed
-
- Chen, J., Jackson, P.K., Kirschner, M.W., and Dutta, A. (1995). Separate domains of p21 involved in the inhibition of Cdk kinase and PCNA. Nature 374, 386–388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

