Echinococcus multilocularis alkaline phosphatase as a marker for metacestode damage induced by in vitro drug treatment with albendazole sulfoxide and albendazole sulfone
- PMID: 11451682
- PMCID: PMC90639
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.8.2256-2262.2001
Echinococcus multilocularis alkaline phosphatase as a marker for metacestode damage induced by in vitro drug treatment with albendazole sulfoxide and albendazole sulfone
Abstract
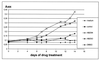
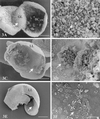
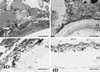
Alveolar echinococcosis (AE) is caused by the metacestode stage of the fox tapeworm Echinococcus multilocularis. The disease affects the human liver and occasionally other organs and is fatal if treatment is unsuccessful. The present chemotherapy of AE is based on the administration of benzimidazole carbamate derivatives, such as mebendazole and albendazole. Albendazole treatment has been found to be ineffective in some cases, parasitostatic rather than parasiticidal, and the recurrence rate is rather high. Therefore, chemotherapy usually involves the lifelong uptake of massive doses of albendazole and new treatment options are urgently needed. In order to avoid costly and time-consuming animal experimentation, a first step in searching for novel parasiticidal compounds could be the in vitro drug screening of novel compounds by employing metacestode cultivation. However, presently used techniques (e.g., transmission electron microscopy) for determination of parasite viability involve costly equipment and time-consuming preparation of rather large amounts of parasite material. We therefore searched for a parasite marker which can be easily traced and the presence or absence of which is indicative of parasite viability. In this study we show that the increase of E. multilocularis alkaline phosphatase activity in culture supernatants during in vitro drug treatment with albendazole derivatives correlates with the progressive degeneration and destruction of the metacestode tissue. The inexpensive and rapid assay presented here will serve as an ideal tool for performing first-round in vitro tests on the efficacy of a large number of antiparasitic compounds.
Figures
References
-
- Ammann R W. Improvement of liver resectional therapy by adjuvant chemotherapy in alveolar hydatid disease. Swiss Echinococcosis Study Group (SESG) Parasitol Res. 1991;77:290–293. - PubMed
-
- Ammann R W, Illitsch N, Marincek B, Freiburghaus A U. Effect of chemotherapy on the larval mass and the long-term course of alveolar echinococcosis. Hepatology. 1994;19:735–742. - PubMed
-
- Ammann R W, Hoffmann A F, Eckert J. Swiss study of chemotherapy of alveolar echinococcosis—review of a 20-year clinical research project. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1999;129:323–332. - PubMed
-
- Ammann R W, Hirsbrunner R, Cotting J, Steiger U, Jacquier P, Eckert J. Recurrence rate after discontinuation of long-term mebendazole therapy in alveolar echinococcosis (preliminary results) Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990;43:506–515. - PubMed
-
- Arme C, Pappas P W, editors. The biology of the Eucestoda. Vol. 2. London, England: Academic Press; 1983. Host-parasite interface; pp. 297–310.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

