Novel class A beta-lactamase Sed-1 from Citrobacter sedlakii: genetic diversity of beta-lactamases within the Citrobacter genus
- PMID: 11451687
- PMCID: PMC90644
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.8.2287-2298.2001
Novel class A beta-lactamase Sed-1 from Citrobacter sedlakii: genetic diversity of beta-lactamases within the Citrobacter genus
Abstract
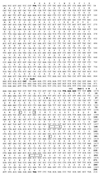
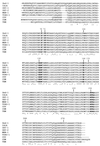
Citrobacter sedlakii 2596, a clinical strain resistant to aminopenicillins, carboxypenicillins, and early cephalosporins such as cephalothin, but remaining susceptible to acylureidopenicillins, carbapenems, and later cephalosporins such as cefotaxime, was isolated from the bile of a patient treated with beta-lactam and quinolone antibiotics. The isolate produced an inducible class A beta-lactamase of pI 8.6, named Sed-1, which was purified. Characterized by a molecular mass of 30 kDa, Sed-1 preferentially hydrolyzed benzylpenicillin, cephalothin, and cloxacillin. The corresponding gene, bla(Sed-1), was cloned and sequenced. Its deduced amino acid sequence shared more than 60% identity with the chromosome-encoded beta-lactamases from Citrobacter koseri (formerly C. diversus) (84%), Klebsiella oxytoca (74%), Serratia fonticola (67%), and Proteus vulgaris (63%) and 71% identity with the plasmid-mediated enzyme MEN-1. A gene coding for a LysR transcriptional regulator was found upstream from bla(Sed-1). This regulator, named SedR, displayed 90% identity with the AmpR sequence of the chromosomal beta-lactamase from C. koseri and 63 and 50% identity with the AmpR sequences of P. vulgaris and Enterobacter cloacae, respectively. By using DNA-DNA hybridization, a bla(Sed-1)-like gene was identified in two reference strains, C. sedlakii (CIP-105037) and Citrobacter rodentium (CIP-104675), but not in the 18 strains of C. koseri studied. Two DNA fragments were amplified and sequenced from the reference strains of C. sedlakii CIP-105037 and C. rodentium CIP-104675 using two primers specific for bla(Sed-1). They shared 98 and 80% identity with bla(Sed-1), respectively, confirming the diversity of the chromosomally encoded class A beta-lactamases found in Citrobacter.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characterization of the chromosomal class A beta-lactamase CKO from Citrobacter koseri.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006 Jan;254(2):285-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2005.00028.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006. PMID: 16445758
-
Characterization of SFO-1, a plasmid-mediated inducible class A beta-lactamase from Enterobacter cloacae.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999 Feb;43(2):307-13. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.2.307. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999. PMID: 9925524 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-encoded narrow-spectrum Ambler class A beta-lactamase GIL-1 from Citrobacter gillenii.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007 Apr;51(4):1365-72. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01152-06. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2007. PMID: 17242148 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of chromosomal beta-lactamases to beta-lactam resistance in enterobacteria.Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Jul-Aug;8 Suppl 3:S292-304. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.supplement_3.s292. Rev Infect Dis. 1986. PMID: 3529322 Review.
-
Beta-lactamase: an ideal reporter system for monitoring gene expression in live eukaryotic cells.Biotechniques. 2007 Jan;42(1):91-6. doi: 10.2144/000112292. Biotechniques. 2007. PMID: 17269490 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and biochemical characterization of the natural chromosome-encoded class A beta-lactamase from Pseudomonas luteola.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jan;54(1):45-51. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00427-09. Epub 2009 Nov 2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 19884377 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of beta-lactamases and their genes (blaA and blaB) in Yersinia intermedia and Y. frederiksenii.BMC Microbiol. 2007 Apr 3;7:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-7-25. BMC Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17407578 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical-genetic analysis and distribution of DES-1, an Ambler class A extended-spectrum beta-lactamase from Desulfovibrio desulfuricans.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Oct;46(10):3215-22. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.10.3215-3222.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 12234847 Free PMC article.
-
Nationwide molecular epidemiology of carbapenemase-producing Citrobacter spp. in France in 2019 and 2020.mSphere. 2023 Dec 20;8(6):e0036623. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00366-23. Epub 2023 Oct 10. mSphere. 2023. PMID: 37815363 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Class A β-Lactamase CzoA by CzoR and IscR in Comamonas testosteroni S44.Front Microbiol. 2017 Dec 22;8:2573. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02573. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29312251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldova E, Schindler J, Nemec A, Sourek J, Urbaskova P. Biochemical indicators of Citrobacter sedlakii. Epidemiol Mikrobiol Imunol. 1995;44:57–64. - PubMed
-
- Aldova E, Schindler J, Sourek J, Nemec A, Urbaskova P. Detection and identification of Citrobacter sedlakii in the Czech Republic. Zentbl Bakteriol. 1997;285:389–396. - PubMed
-
- Altschul S F, Gish W, Miller W, Myers E W, Lipman D J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Amicosante G, Frere J M, Franceschini N, Oratore A, Strom R. Some molecular properties of Citrobacter diversus beta-lactamases. J Chemother. 1991;3:83–85. - PubMed
-
- Appel R D, Bairoch A, Hochstrasser D F. A new generation of information retrieval tools for biologists: the example of the ExPASy WWW server. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994;19:258–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

