Resistance to moxifloxacin in toxigenic Clostridium difficile isolates is associated with mutations in gyrA
- PMID: 11451695
- PMCID: PMC90652
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.8.2348-2353.2001
Resistance to moxifloxacin in toxigenic Clostridium difficile isolates is associated with mutations in gyrA
Abstract
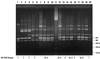
Clostridium difficile is the etiological agent of antibiotic-associated colitis and the most common cause of hospital-acquired infectious diarrhea. Fluoroquinolones such as ciprofloxacin are associated with lower risks of C. difficile-associated diarrhea. In this study, we have analyzed 72 C. difficile isolates obtained from patients with different clinical courses of disease, such as toxic megacolon and relapses; the hospital environment; public places; and horses. They were investigated for their susceptibilities to moxifloxacin (MXF), metronidazole (MEO), and vancomycin (VAN). Mutants highly resistant to fluoroquinolones were selected in vitro by stepwise exposure to increasing concentrations of MXF. The resulting mutants were analyzed for the presence of mutations in the quinolone resistance-determining regions of DNA gyrase (gyrA), the production of toxins A and B, and the epidemiological relationship of these isolates. These factors were also investigated using PCR-based methods. All strains tested were susceptible to MEO and VAN. Twenty-six percent of the clinical isolates (19 of 72) were highly resistant to MXF (MIC > or = 16 microg/ml). Fourteen of these 19 strains contained nucleotide changes resulting in amino acid substitutions at position 83 in the gyrA protein. Resistant strains selected in vitro did not contain mutations at that position. These findings indicate that resistance to MXF in a majority of cases may be due to amino acid substitution in the gyrA gene.
Figures

References
-
- Ackermann G, Schaumann R, Pless B, Claros M C, Goldstein E J C, Rodloff A C. Comparative activity of moxifloxacin in vitro against obligately anaerobic bacteria. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2000;19:228–232. - PubMed
-
- Banno Y, Kobayashi T, Kono H, Watanabe K, Veno K, Nozawa Y. Biochemical characterisation and biological action of two toxins (D-1 and D-2) from Clostridium difficile. Rev Infect Dis. 1984;6:S11–S20. - PubMed
-
- Brosius J, Dull T J, Sleeter D D, Noller H F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981;148:107–127. - PubMed
-
- Cambau E, Gutmann L. Mechanisms of resistance to quinolones. Drugs. 1993;45:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Cohen S H, Tang Y J, Muenzner J, Gumerlock P H, Silva J., Jr Isolation of various genotypes of Clostridium difficile from patients and the environment in an oncology ward. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;24:889–893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

