Mutation in the DNA gyrase A Gene of Escherichia coli that expands the quinolone resistance-determining region
- PMID: 11451702
- PMCID: PMC90659
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.8.2378-2380.2001
Mutation in the DNA gyrase A Gene of Escherichia coli that expands the quinolone resistance-determining region
Abstract
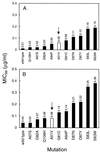
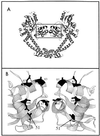
In three Escherichia coli mutants, a change (Ala-51 to Val) in the gyrase A protein outside the standard quinolone resistance-determining region (QRDR) lowered the level of quinolone susceptibility more than changes at amino acids 67, 82, 84, and 106 did. Revision of the QRDR to include amino acid 51 is indicated.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quinolone resistance-determining region in the DNA gyrase gyrA gene of Escherichia coli.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jun;34(6):1271-2. doi: 10.1128/AAC.34.6.1271. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990. PMID: 2168148 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the NH2-terminal 83rd amino acid of Escherichia coli GyrA in quinolone-resistance.Microbiol Immunol. 1995;39(4):243-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1995.tb02196.x. Microbiol Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7651238
-
Analysis of the NH2-terminal 87th amino acid of Escherichia coli GyrA in quinolone-resistance.Microbiol Immunol. 1995;39(7):517-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1995.tb02236.x. Microbiol Immunol. 1995. PMID: 8569537
-
DNA gyrase as a drug target.Biochem Soc Trans. 1999 Feb;27(2):48-53. doi: 10.1042/bst0270048. Biochem Soc Trans. 1999. PMID: 10093705 Review. No abstract available.
-
Molecular epidemiological analysis of quinolone-resistant Escherichia coli causing bacteremia in neutropenic patients with leukemia in Korea.Clin Infect Dis. 1997 Dec;25(6):1385-91. doi: 10.1086/516132. Clin Infect Dis. 1997. PMID: 9431383 Review.
Cited by
-
Topoisomerase II and IV quinolone resistance-determining regions in Stenotrophomonas maltophilia clinical isolates with different levels of quinolone susceptibility.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Mar;46(3):665-71. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.3.665-671.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 11850246 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species accelerate de novo acquisition of antibiotic resistance in E. coli.iScience. 2023 Oct 31;26(12):108373. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108373. eCollection 2023 Dec 15. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38025768 Free PMC article.
-
An allele of gyrA prevents Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium from using succinate as a carbon source.J Bacteriol. 2006 Apr;188(8):3126-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.188.8.3126-3129.2006. J Bacteriol. 2006. PMID: 16585773 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation rate and evolution of fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli isolates from patients with urinary tract infections.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Oct;47(10):3222-32. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.10.3222-3232.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 14506034 Free PMC article.
-
Type II topoisomerase quinolone resistance-determining regions of Aeromonas caviae, A. hydrophila, and A. sobria complexes and mutations associated with quinolone resistance.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Feb;46(2):350-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.2.350-359.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 11796341 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friedman S M, Droffner M L, Yamamoto N. Thermotolerant nalidixic acid-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. Curr Microbiol. 1991;22:311–316.
-
- Friedman S M, Malik M, Drlica K. DNA supercoiling in a thermotolerant mutant of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1995;248:417–422. - PubMed
-
- Jendrisak J, Young R, Engel J. In: Guide to molecular cloning techniques. Berger S, Kimmel A, editors. New York, N.Y: Academic Press, Inc.; 1978. pp. 359–371.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

