RME-8, a conserved J-domain protein, is required for endocytosis in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 11451999
- PMCID: PMC55649
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.7.2011
RME-8, a conserved J-domain protein, is required for endocytosis in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
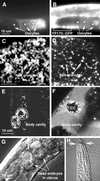
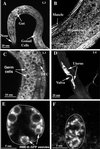
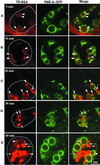
By genetic analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans mutants defective in yolk uptake, we have identified new molecules functioning in the endocytosis pathway. Here we describe a novel J-domain-containing protein, RME-8, identified by such genetic analysis. RME-8 is required for receptor-mediated endocytosis and fluid-phase endocytosis in various cell types and is essential for C. elegans development and viability. In the macrophage-like coelomocytes, RME-8 localizes to the limiting membrane of large endosomes. Endocytosis markers taken up by the coelomocytes rapidly accumulate in these large RME-8-positive endosomes, concentrate in internal subendosomal structures, and later appear in RME-8-negative lysosomes. rme-8 mutant coelomocytes fail to accumulate visible quantities of endocytosis markers. These observations show that RME-8 functions in endosomal trafficking before the lysosome. RME-8 homologues are found in multicellular organisms from plants to humans but not in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. These sequence homologies suggest that RME-8 fulfills a conserved function in multicellular organisms.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Regulation of endocytic recycling by C. elegans Rab35 and its regulator RME-4, a coated-pit protein.EMBO J. 2008 Apr 23;27(8):1183-96. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.54. Epub 2008 Mar 20. EMBO J. 2008. PMID: 18354496 Free PMC article.
-
The DnaJ-domain protein RME-8 functions in endosomal trafficking.J Biol Chem. 2005 Dec 2;280(48):40135-43. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M505036200. Epub 2005 Sep 22. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 16179350
-
Receptor-mediated endocytosis in the Caenorhabditis elegans oocyte.Mol Biol Cell. 1999 Dec;10(12):4311-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.10.12.4311. Mol Biol Cell. 1999. PMID: 10588660 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering endocytosis in Caenorhabditis elegans.Traffic. 2002 Jan;3(1):11-9. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2002.30103.x. Traffic. 2002. PMID: 11872138 Review.
-
Mammalian Unc-13 homologues as possible regulators of neurotransmitter release.Biochem Soc Trans. 1996 Aug;24(3):661-6. doi: 10.1042/bst0240661. Biochem Soc Trans. 1996. PMID: 8878822 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
TBC-8, a putative RAB-2 GAP, regulates dense core vesicle maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2012;8(5):e1002722. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002722. Epub 2012 May 24. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22654674 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock proteins: cellular and molecular mechanisms in the central nervous system.Prog Neurobiol. 2010 Oct;92(2):184-211. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.05.002. Epub 2010 Jun 4. Prog Neurobiol. 2010. PMID: 20685377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The conserved transmembrane RING finger protein PLR-1 downregulates Wnt signaling by reducing Frizzled, Ror and Ryk cell-surface levels in C. elegans.Development. 2014 Feb;141(3):617-28. doi: 10.1242/dev.101600. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Development. 2014. PMID: 24401370 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle budding is inhibited by redundant regulators of TAT-5 flippase localization and phospholipid asymmetry.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 6;115(6):E1127-E1136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1714085115. Epub 2018 Jan 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29367422 Free PMC article.
-
Intracellular trafficking pathways in silver nanoparticle uptake and toxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nanotoxicology. 2016 Sep;10(7):831-5. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2015.1110759. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Nanotoxicology. 2016. PMID: 26559224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams MD, et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 2000;287:2185–2195. - PubMed
-
- Bettinger JC, Lee K, Rougvie AE. Stage-specific accumulation of the terminal differentiation factor LIN-29 during Caenorhabditis elegans development. Development. 1996;122:2517–2527. - PubMed
-
- Christoforidis S, McBride HM, Burgoyne RD, Zerial M. The Rab5 effector EEA1 is a core component of endosome docking. Nature. 1999;397:621–625. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

