Vaccinia virus DNA replication occurs in endoplasmic reticulum-enclosed cytoplasmic mini-nuclei
- PMID: 11452001
- PMCID: PMC55651
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.7.2031
Vaccinia virus DNA replication occurs in endoplasmic reticulum-enclosed cytoplasmic mini-nuclei
Abstract
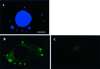
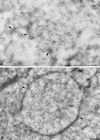
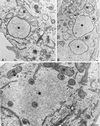
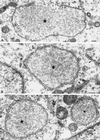
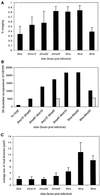
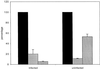
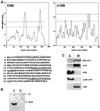
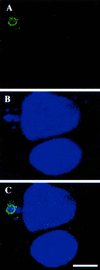
Vaccinia virus (vv), a member of the poxvirus family, is unique among most DNA viruses in that its replication occurs in the cytoplasm of the infected host cell. Although this viral process is known to occur in distinct cytoplasmic sites, little is known about its organization and in particular its relation with cellular membranes. The present study shows by electron microscopy (EM) that soon after initial vv DNA synthesis at 2 h postinfection, the sites become entirely surrounded by membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Complete wrapping requires ~45 min and persists until virion assembly is initiated at 6 h postinfection, and the ER dissociates from the replication sites. [(3)H]Thymidine incorporation at different infection times shows that efficient vv DNA synthesis coincides with complete ER wrapping, suggesting that the ER facilitates viral replication. Proteins known to be associated with the nuclear envelope in interphase cells are not targeted to these DNA-surrounding ER membranes, ruling out a role for these molecules in the wrapping process. By random green fluorescent protein-tagging of vv early genes of unknown function with a putative transmembrane domain, a novel vv protein, the gene product of E8R, was identified that is targeted to the ER around the DNA sites. Antibodies raised against this vv early membrane protein showed, by immunofluorescence microscopy, a characteristic ring-like pattern around the replication site. By electron microscopy quantitation the protein concentrated in the ER surrounding the DNA site and was preferentially targeted to membrane facing the inside of this site. These combined data are discussed in relation to nuclear envelope assembly/disassembly as it occurs during the cell cycle.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The vaccinia virus I3L gene product is localized to a complex endoplasmic reticulum-associated structure that contains the viral parental DNA.J Virol. 2003 May;77(10):6014-28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.10.6014-6028.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12719593 Free PMC article.
-
The Vaccinia virus E8R gene product: a viral membrane protein that is made early in infection and packaged into the virions' core.J Virol. 2002 Oct;76(19):9773-86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.19.9773-9786.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12208956 Free PMC article.
-
Direct formation of vaccinia virus membranes from the endoplasmic reticulum in the absence of the newly characterized L2-interacting protein A30.5.J Virol. 2013 Nov;87(22):12313-26. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02137-13. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24027302 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic organization of POXvirus DNA replication.Traffic. 2005 Oct;6(10):839-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00324.x. Traffic. 2005. PMID: 16138898 Review.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum: The Favorite Intracellular Niche for Viral Replication and Assembly.Viruses. 2016 Jun 7;8(6):160. doi: 10.3390/v8060160. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27338443 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orthopoxvirus genes that mediate disease virulence and host tropism.Adv Virol. 2012;2012:524743. doi: 10.1155/2012/524743. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Adv Virol. 2012. PMID: 22899927 Free PMC article.
-
Pox proteomics: mass spectrometry analysis and identification of Vaccinia virion proteins.Virol J. 2006 Mar 1;3:10. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-3-10. Virol J. 2006. PMID: 16509968 Free PMC article.
-
Poxvirus Recombination.Pathogens. 2022 Aug 9;11(8):896. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11080896. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36015016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaccinia virus L2 protein associates with the endoplasmic reticulum near the growing edge of crescent precursors of immature virions and stabilizes a subset of viral membrane proteins.J Virol. 2011 Dec;85(23):12431-41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05573-11. Epub 2011 Sep 14. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21917978 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral effect of Hornstedtia bella Škorničk essential oil from the whole plant against vaccinia virus (VV).Nat Prod Res. 2021 Dec;35(24):5674-5680. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2020.1824228. Epub 2020 Sep 25. Nat Prod Res. 2021. PMID: 32975126 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Banham AH, Leader DP, Smith GL. Phosphorylation of ribosomal proteins by the vaccinia virus B1R protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1993;321:27–31. - PubMed
-
- Banham AH, Smith GL. Vaccinia virus gene B1R encodes a 34-kDa serine/threonine protein kinase that localizes in cytoplasmic factories and is packaged into virions. Virology. 1992;191:803–812. - PubMed
-
- Beaud G, Beaud R. Preferential virosomal location of underphosphorylated H5R protein synthesized in vaccinia virus-infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1997;78:3297–3302. - PubMed
-
- Beaud G, Sharif A, Topa-Masse A, Leader DP. Ribosomal protein S2/Sa kinase purified from HeLa cells infected with vaccinia virus corresponds to the B1R kinase and phosphorylates in vitro the viral ssDNA-binding protein. J Gen Virol. 1994;75:283–293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

