Activation of Rhoa and ROCK are essential for detachment of migrating leukocytes
- PMID: 11452009
- PMCID: PMC55668
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.12.7.2137
Activation of Rhoa and ROCK are essential for detachment of migrating leukocytes
Abstract
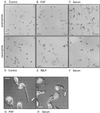
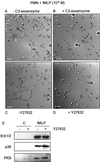
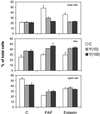
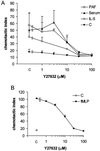
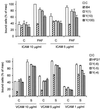
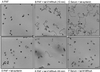
Detachment of the rear of the cell from its substratum is an important aspect of locomotion. The signaling routes involved in this adhesive release are largely unknown. One of the few candidate proteins to play a role is RhoA, because activation of RhoA in many cell types leads to contraction, a mechanism probably involved in detachment. To study the role of RhoA in detachment regulation, we analyzed several subsets of expert migratory leukocytes by video microscopy. In contrast to fast-migrating neutrophils, eosinophils do not detach the rear of the cell unless stimulated with serum. When measuring the amount of active RhoA, with the use of a GST-Rhotekin pulldown assay, we found that serum is an excellent activator of RhoA in granulocytes. Inhibition of RhoA or one of Rho's target proteins, the kinase ROCK, in neutrophils leads to the phenotype seen in eosinophils: the rear of the cell is firmly attached to the substratum, whereas the cell body is highly motile. ROCK-inhibition leads to impaired migration of granulocytes in filters, on glass, and through endothelial monolayers. Also, the ROCK signaling pathway is involved in changes of integrin-mediated adhesion. Eosinophil transduction by a tat-fusion construct containing active RhoA resulted in detachment stimulation in the presence of chemoattractant. From these results we conclude that activation of the RhoA-ROCK pathway is essential for detachment of migratory leukocytes.
Figures

References
-
- Amano M, Ito M, Kimura K, Fukata Y, Chihara K, Nakano T, Matsuura Y, Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) J Biol Chem. 1996;271:20246–20249. - PubMed
-
- Aspenström P. Effectors for the Rho GTPases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1999;11:95–102. - PubMed
-
- Essler M, Amano M, Kruse HJ, Kaibuchi K, Weber PC, Aepfelbacher M. Thrombin inactivates myosin light chain phosphatase via Rho and its target Rho kinase in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:21867–21874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

