Telomerase activation by histone deacetylase inhibitor in normal cells
- PMID: 11452025
- PMCID: PMC55810
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.14.3006
Telomerase activation by histone deacetylase inhibitor in normal cells
Abstract
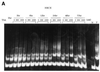
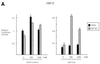
Although telomerase activity is known to be regulated mainly at the level of transcription of the human telomerase catalytic subunit (hTERT) gene, the molecular mechanism underlying tumor-specific expression of telomerase remains unclear. Emerging evidence suggests that reversible acetylation of nucleosomal histones and the resultant changes in the chromatin structure are important processes in gene transcription. In particular, histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors activate the transcription of certain genes by altering the acetylation status of nucleosomal histones. The present study examines the effects of HDAC inhibitor on hTERT gene transcription. Treatment with tricostatin A (TSA) induced significant activation of hTERT mRNA expression and telomerase activity in normal cells, but not in cancer cells. Transient expression assays revealed that TSA activates the hTERT promoter. Furthermore, the proximal 181 bp core promoter of hTERT, which contains two c-Myc and five Sp1 sites, was determined to be the responsible element. Overexpression of Sp1 enhanced responsiveness to TSA, and mutation of Sp1 sites, but not c-Myc sites, of the core promoter of hTERT abrogated this activation. Introduction of the dominant-negative form of the Sp family inhibited TSA activation. These results indicate that HDAC inhibitor activates the hTERT promoter in normal cells, in which Sp1 plays a key role. This finding suggests one way whereby histone deacetylation may be involved in silencing the hTERT gene in normal cells.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A derepresses the telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) gene in human cells.Exp Cell Res. 2002 Mar 10;274(1):25-34. doi: 10.1006/excr.2001.5462. Exp Cell Res. 2002. PMID: 11855854
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors suppress telomerase reverse transcriptase mRNA expression in prostate cancer cells.Int J Cancer. 2002 Feb 10;97(5):621-5. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10082. Int J Cancer. 2002. PMID: 11807787
-
Sp1 and Sp3 recruit histone deacetylase to repress transcription of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) promoter in normal human somatic cells.J Biol Chem. 2002 Oct 11;277(41):38230-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206064200. Epub 2002 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12151407
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors: inducers of differentiation or apoptosis of transformed cells.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000 Aug 2;92(15):1210-6. doi: 10.1093/jnci/92.15.1210. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000. PMID: 10922406 Review.
-
Understanding and exploiting hTERT promoter regulation for diagnosis and treatment of human cancers.Cancer Sci. 2008 Aug;99(8):1528-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00878.x. Cancer Sci. 2008. PMID: 18754863 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human telomerase inhibitors from microbial source.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Sep;31(9):1329-41. doi: 10.1007/s11274-015-1893-3. Epub 2015 Jul 1. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26130439 Review.
-
Histone deacetylation is directly involved in desilencing the expression of the catalytic subunit of telomerase in normal lung fibroblast.J Cell Mol Med. 2005 Jul-Sep;9(3):662-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2005.tb00496.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16202213 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and epigenetic trends in telomere research: a novel way in immunoepigenetics.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Nov;72(21):4095-109. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1991-2. Epub 2015 Jul 20. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26190020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer-Specific Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase (TERT) Promoter Mutations: Biological and Clinical Implications.Genes (Basel). 2016 Jul 18;7(7):38. doi: 10.3390/genes7070038. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27438857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomerase Regulation: A Role for Epigenetics.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 10;13(6):1213. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061213. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33802026 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harley C.B., Futcher,A.B. and Greider,C.W. (1990) Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature, 345, 458–460. - PubMed
-
- Watson J.D. (1972) Origin of concatemeric T7 DNA. Nature, 239, 197–201. - PubMed
-
- Kim N.W., Piatyszek,M.A., Prowse,K.R., Harley,C.B., West,M.D., Ho,P.L., Coviello,G.M., Wright,W.E., Weinrich,S.L. and Shay,J.W. (1994) Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science, 266, 2011–2015. - PubMed
-
- Meyerson M., Counter,C.M., Eaton,E.N., Ellisen,L.W., Steiner,P., Caddle,S.D., Ziaugra,L., Beijersbergen,R.L., Davidoff,M.J., Liu,Q. et al. (1997) hEST2, the putative human telomerase catalytic subunit gene, is up-regulated in tumor cells and during immortalization. Cell, 90, 785–795. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura T.M., Morin,G.B., Chapman,K.B., Weinrich,S.L., Andrews,W.H., Lingner,J., Harley,C.B. and Cech,T.R. (1997) Telomerase catalytic subunit homologs from fission yeast and human. Science, 277, 955–959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

