Genomic cloning of the Hsc71 gene in the hermaphroditic teleost Rivulus marmoratus and analysis of its expression in skeletal muscle: identification of a novel muscle-preferred regulatory element
- PMID: 11452029
- PMCID: PMC55811
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.14.3041
Genomic cloning of the Hsc71 gene in the hermaphroditic teleost Rivulus marmoratus and analysis of its expression in skeletal muscle: identification of a novel muscle-preferred regulatory element
Abstract
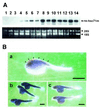
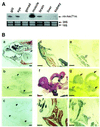
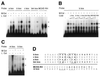
To further our understanding of the role of stress proteins in development as well as in adaptation of fish to adverse environmental conditions, we undertook molecular analyses of stress protein encoding genes from the hermaphroditic teleost Rivulus marmoratus. We isolated a genomic clone containing the Hsc71 gene (rm-hsc71m) and its upstream sequences. rm-Hsc71m is not induced by external stress, but is enriched in a tissue-specific manner during early development. In adult, the strongest expression appeared in skeletal muscle, whereas lower expression was seen in the gill, eye and brain. To understand the regulatory basis of high muscle expression of rm-hsc71m, transfection of R.marmoratus muscle tissue was performed using 5' deletion fragments containing the rm-hsc71m promoter driving EGFP expression. An upstream region from -2.7 to -1.9 kb was identified as a muscle-specific regulatory region. Within this region, we identified at least three sites with the novel sequence TGTnACA interacting with a fish muscle factor having an M(r) of 32 000. Our data indicate that rm-hsc71m expression in skeletal muscle is controlled by a muscle-specific regulatory element containing this novel motif.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genomic cloning of a heat shock cognate 71-1 gene (HSC71-1) from the hermaphroditic fish Rivulus marmoratus (Cyprinodontiformes, Rivulidae).DNA Seq. 2004 Feb;15(1):33-8. doi: 10.1080/10425170310001659393. DNA Seq. 2004. PMID: 15354352
-
Characterization of the human glycogenin-1 gene: identification of a muscle-specific regulatory domain.Gene. 1999 Jul 8;234(2):217-26. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(99)00211-5. Gene. 1999. PMID: 10395894
-
Genomic structure of c-Ki-ras proto-oncogene of the hermaphroditic fish Rivulus marmoratus (teleostei: Rivulidae).Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1995 Jan;35(1):57-63. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1995. PMID: 7735140
-
Absence of the intron-D-exon of c-Ha-ras oncogene in the hermaphroditic fish Rivulus marmoratus (Teleostei: Rivulidae).Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1994 Nov;34(5):921-6. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1994. PMID: 7703908
-
Cloning, expression profile, and genomic organization of the mouse STAP/A170 gene.Genomics. 1999 Aug 15;60(1):87-95. doi: 10.1006/geno.1999.5902. Genomics. 1999. PMID: 10458914
Cited by
-
Isolation of a Latimeria menadoensis heat shock protein 70 (Lmhsp70) that has all the features of an inducible gene and encodes a functional molecular chaperone.Mol Genet Genomics. 2009 Aug;282(2):185-96. doi: 10.1007/s00438-009-0456-4. Epub 2009 May 15. Mol Genet Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19444470
-
Identification of a novel cognate cytosolic Hsp70 gene (MnHsc70-2) from oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense and comparison of its expressions with the first cognate Hsc70 (MnHsc70-1) under different stresses.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2014 Nov;19(6):949-61. doi: 10.1007/s12192-014-0519-2. Epub 2014 May 24. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2014. PMID: 24859888 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Hsp70 in the mud crab, Scylla paramamosain in response to bacterial, osmotic, and thermal stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013 Jul;18(4):475-82. doi: 10.1007/s12192-013-0402-6. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013. PMID: 23325574 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-stress properties and two HSP70s mRNA expressions of blunt snout bream (Megalobrama amblycephala) fed with all-plant-based diet.Fish Physiol Biochem. 2014 Jun;40(3):817-25. doi: 10.1007/s10695-013-9888-1. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Fish Physiol Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24254296
-
Genomic cloning of mud loach Misgurnus mizolepis (Cypriniformes, Cobitidae) beta-actin gene and usefulness of its promoter region for fish transgenesis.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2003 May-Jun;5(3):244-52. doi: 10.1007/s10126-002-0066-1. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2003. PMID: 14502396
References
-
- Morimoto R.I., Tissieres,A. and Georgopoulos,C. (1994) The Biology of Heat Shock Proteins and Molecular Chaperones. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
-
- Feder M.E. and Hofmann,G.E. (1999) Heat-shock proteins, molecular chaperones, and the stress response: evolutionary and ecological physiology. Annu. Rev. Physiol., 61, 243–282. - PubMed
-
- Sorger P.K. (1991) Heat shock factor and the heat shock response. Cell, 65, 363–366. - PubMed
-
- Boorstein W.R., Ziegelhoffer,T. and Craig,E.A. (1994) Molecular evolution of the HSP70 multigene family. J. Mol. Evol., 38, 1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions

