The autism genetic resource exchange: a resource for the study of autism and related neuropsychiatric conditions
- PMID: 11452364
- PMCID: PMC1235320
- DOI: 10.1086/321292
The autism genetic resource exchange: a resource for the study of autism and related neuropsychiatric conditions
Figures
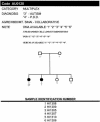
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Autism Genetic Resource Exchange, http://www.agre.org/
-
- Cure Autism Now, http://www.canfoundation.org/
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th ed–revised. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
-
- Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, Yuzda E, Rutter M (1995) Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med 25:63–77 - PubMed
-
- Barrett S, Beck JC, Bernier R, Bisson E, Braun TA, Casavant TL, Childress D, et al (1999) An autosomal genomic screen for autism: collaborative linkage study of autism. Am J Med Genet 88:609–615 - PubMed
-
- Brown WT, Jenkins EC, Cohen IL, Fisch GS, Wolf-Schein EG, Gross A, Waterhouse L (1986) Fragile X and autism: a multicenter survey. Am J Med Genet 23:341–352 - PubMed
-
- Bryson SE, Clark BS, Smith IM (1988) First report of a Canadian epidemiological study of autistic syndromes. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 29:433–445 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

