Influence of the CYP2D6*10 allele on the metabolism of mexiletine by human liver microsomes
- PMID: 11453897
- PMCID: PMC2014511
- DOI: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.01411.x
Influence of the CYP2D6*10 allele on the metabolism of mexiletine by human liver microsomes
Abstract
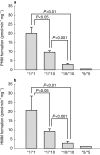
Aims: To study the influence of CYP2D6*10 on the formation of p-hydroxymexiletine (PHM) and hydroxymethylmexiletine (HMM) using microsomes from human liver of known genotypes.
Methods: Microsomes from human livers of genotype CYP2D6*1/*1 (n = 5), *1/*10 (n = 6) and *10/*10 (n = 6) were used in this study. The formation of PHM and HMM was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography.
Results: The formation rates of PHM and HMM were decreased by more than 50% and 85% in CYP2D6*1/*10 and *10/*10 microsomes, respectively, compared with *1/*1 microsomes.
Conclusions: The metabolism of mexiletine to form PHM and HMM appears to be impaired to a significant extent in human liver microsomes from hetero- and homozygotes of CYP2D6*10.
Figures
References
-
- Turgeon J, Fiset C, Giguere R, et al. Influence of debrisoquine phenotype and of quinidine on mexiletine disposition in man. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991;259:789–798. - PubMed
-
- Johansson I, Oscarson M, Yue QY, Bertilsson L, Sjoqvist F, Ingelman-Sundberg M. Genetic analysis of the Chinese cytochrome P4502D locus: characterization of variant CYP2D6 genes present in subjects with diminished capacity for debrisoquine hydroxylation. Mol Pharmacol. 1994;46:452–459. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources