Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after bone marrow transplantation: the role of pre-transplant radiation conditioning and local cytokine dysregulation in promoting lung inflammation and fibrosis
- PMID: 11454101
- PMCID: PMC2517701
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2001.iep0082-0101-x
Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome after bone marrow transplantation: the role of pre-transplant radiation conditioning and local cytokine dysregulation in promoting lung inflammation and fibrosis
Abstract
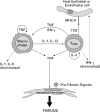
Pulmonary complications and graft-vs.-host disease (GVHD) remain severe threats to survival after bone marrow transplantation (BMT). Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome (IPS) accounts for nearly 50% of all the cases of interstitial pneumonitis after BMT. IPS is characterized by an early inflammatory phase followed by chronic inflammation and fibrosis of lung tissue; however, the immunopathogenesis of this disease is not yet clearly understood. This biphasic syndrome has been reported to be associated with pre-transplant radiation conditioning in some studies while others have suggested that GVHD or autoimmune phenomena may be responsible for its development. The early post-BMT phase is characterized by the presence of inflammatory cytokines whose net effect is to promote lymphocyte influx into lungs with minimal fibrosis, that leads to an acute form of graft-vs.-host reaction-mediated pulmonary tissue damage. Gradual changes over time in leucocyte influx and activation lead to dysregulated wound repair mechanisms resulting from the shift in the balance of cytokines that promote fibrosis. Using data from new animal models of IPS and information from studies of human IPS, we hypothesize that cytokine-modulated immunological mechanisms which occur during the acute and chronic phases after bone marrow transplantation lead to the development of the progressive, inflammatory, and fibrotic lung disease typical of idiopathic pneumonia syndrome.
Figures


References
-
- Agelli M, Wahl SM. Cytokines and fibrosis. Clin. Exp Rheumatol. 1986;4:379–388. - PubMed
-
- Allen RD, Staley TA, Sidman CL. Differential cytokine expression in acute and chronic murine graft-versus-host disease. European J. Immunology. 1993;23:333–337. - PubMed
-
- Anscher MS, Murase T, Prescott DM, et al. Changes in plasma TGFβ levels during pulmonary radiotherapy as a predictor of the risk of developing radiation pneumonitis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994;30:671–676. - PubMed
-
- Antin JH, Ferrara JLM. Cytokine dysregulation and acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 1992;80:2964–2968. - PubMed
-
- Ash RC, Casper JT, Chitambar CR, et al. Successful allogeneic transplantation of T-cell-depleted bone marrow from closely HLA-matched unrelated donors. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990;322:485–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

