Relationship between psychological state and level of activity of extrinsic gut innervation in patients with a functional gut disorder
- PMID: 11454796
- PMCID: PMC1728413
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.49.2.209
Relationship between psychological state and level of activity of extrinsic gut innervation in patients with a functional gut disorder
Abstract
Background: Anxiety and depression are known to be associated with alterations in central autonomic activity, and this may manifest as a functional gut disturbance. However, the final expression of motility disturbance is non-specific and non-quantifiable. This study examines the relationship between psychological state and psychosocial functioning with a new direct measure of the level of activity of extrinsic autonomic gut innervation, rectal mucosal Doppler blood flow.
Materials and methods: Thirty four female patients (mean age 36 years, range 19--45) with constipation for greater than five years and 19 healthy women (mean age 38 years, range 21--60) were studied. They completed the general health questionnaire-28 point scale (GHQ-28; psychosocial functioning) and the Bem sex role inventory (BSRI; an index of women's psychological feelings about their own femininity). On the same day they underwent measurement of rectal mucosal Doppler blood flow, a new validated measure of the activity of gut extrinsic nerve innervation. Measurements were made during the follicular phase and in the fasted state.
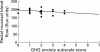
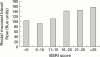
Results: Women with constipation scored higher on the total GHQ-28 score and the somatisation (p=0.05) and anxiety (p=0.05) subscales of the GHQ-28. There was a negative correlation between mucosal blood flow and GHQ somatisation subscale (r=-0.45, p<0.005), anxiety (r=-0.38, p<0.05), and depression (r=-0.40, p<0.01) scores in women with constipation. Although constipated women scored no higher than controls on the BSRI, there was a significant negative correlation between blood flow and BSRI score (r=-0.49, p<0.005) for constipated women.
Conclusions: General psychosocial function, somatisation, anxiety, depression, and feelings about female role are impaired in women with constipation and associated with altered rectal mucosal blood flow, a measure of extrinsic gut innervation. These findings suggest that psychological factors are likely to influence gut function via autonomic efferent neural pathways.
Figures

Comment in
-
Descartes and the gut: "I'm pink therefore I am".Gut. 2001 Aug;49(2):165-6. doi: 10.1136/gut.49.2.165. Gut. 2001. PMID: 11454788 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
