Arginine induced acute pancreatitis alters the actin cytoskeleton and increases heat shock protein expression in rat pancreatic acinar cells
- PMID: 11454802
- PMCID: PMC1728407
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.49.2.241
Arginine induced acute pancreatitis alters the actin cytoskeleton and increases heat shock protein expression in rat pancreatic acinar cells
Abstract
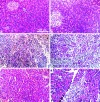
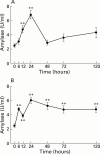
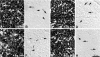
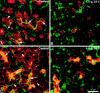
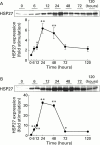
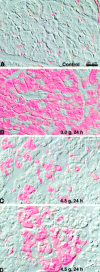
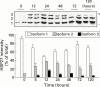
Arginine induced acute pancreatitis was evaluated as a novel and distinct form of experimental pancreatitis with particular attention to the actin cytoskeleton and expression of heat shock or stress proteins. Arginine induced a dose related necrotising pancreatitis in rats, as shown by histological evaluation, and an increase in serum amylase. Severe pancreatitis induced by 4.5 g/kg arginine was accompanied by dramatic changes in the actin cytoskeleton, as visualised with rhodamine phallodin. Intermediate filaments were also disrupted, as visualised by cytokeratin 8/18 immunocytochemistry. Arginine pancreatitis was accompanied by a stress response with a large increase in the small heat shock protein HSP27, as well as HSP70, peaking at 24 hours and localised to acinar cells. There was a lower increase in HSP60 and HSP90 and no effect on GRP78. HSP27 was also shifted to phosphorylated forms during pancreatitis. A lower dose of arginine (3.0 g/kg) induced less pancreatitis but a larger increase in HSP70 and HSP27 expression and phosphorylation of HSP27. Thus HSP expression can be overwhelmed by severe damage. The present work in conjunction with earlier work on caerulein induced pancreatitis indicates that changes in the actin cytoskeleton are an early component in experimental pancreatitis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hyperthermia induces multiple pancreatic heat shock proteins and protects against subsequent arginine-induced acute pancreatitis in rats.Digestion. 2002;65(2):118-26. doi: 10.1159/000057713. Digestion. 2002. PMID: 12021485
-
Expression of heat shock proteins in medulloblastoma.J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2013 Nov;12(5):452-7. doi: 10.3171/2013.7.PEDS1376. Epub 2013 Aug 30. J Neurosurg Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23992239
-
Expression of heat shock proteins (HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, HSP90, GRP78, GRP94) in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Apr 14;11(14):2072-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i14.2072. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15810071 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical localization and expression of heat shock proteins (HSP27, HSP60, HSP70, and HSP90) during the oestrous cycle, pregnancy, and lactation in rat ovaries.Acta Histochem. 2024 Apr;126(3):152157. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2024.152157. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Acta Histochem. 2024. PMID: 38581753 Review.
-
Alteration and role of heat shock proteins in acute pancreatitis.J Dig Dis. 2010 Oct;11(5):277-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2010.00450.x. J Dig Dis. 2010. PMID: 20883423 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of curcumin on oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in L-arginine induced acute pancreatitis in mice.Heliyon. 2019 Aug 27;5(8):e02222. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02222. eCollection 2019 Aug. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31485503 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of Hub Genes in Acute Pancreatitis and Hypertriglyceridemia.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022 Feb 24;15:559-577. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S349528. eCollection 2022. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022. PMID: 35237056 Free PMC article.
-
Total parenteral nutrition attenuates cerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats.Pancreas. 2010 Apr;39(3):377-84. doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181bb908e. Pancreas. 2010. PMID: 19904225 Free PMC article.
-
Acute pancreatitis induces a transient hypercoagulable state in murine models.Pancreatology. 2023 Apr;23(3):306-313. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2023.02.007. Epub 2023 Mar 3. Pancreatology. 2023. PMID: 36898897 Free PMC article.
-
L-arginine-induced experimental pancreatitis.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Jul 15;10(14):2003-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i14.2003. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15237423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
