Is myosin phosphatase regulated in vivo by inhibitor-1? Evidence from inhibitor-1 knockout mice
- PMID: 11454956
- PMCID: PMC2278711
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00357.x
Is myosin phosphatase regulated in vivo by inhibitor-1? Evidence from inhibitor-1 knockout mice
Abstract
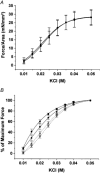
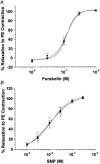
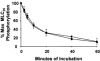
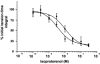
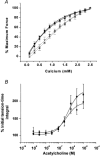
1. The Ca(2+) sensitivity of smooth muscle contractility is modulated via regulation of phosphatase activity. Protein phosphatase inhibitor-1 (I-1) is the classic type-1 phosphatase inhibitor, but its presence and role in cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) modulation of smooth muscle is unclear. To address the relevance of I-1 in vivo, we investigated smooth muscle function in a mouse model lacking the I-1 protein (I-1((-/-)) mice). 2. Significant amounts of I-1 protein were detected in the wild-type (WT) mouse aorta and could be phosphorylated by PKA, as indicated by (32)P-labelled aortic extracts from WT mice. 3. Despite the significant presence of I-1 in WT aorta, phenylephrine and KCl concentration- isometric force relations in the presence or absence of the PKA pathway activator isoproterenol (isoprenaline) were unchanged compared to I-1((-/-)) aorta. cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) relaxation pathways were also not different. Consistent with these findings, dephosphorylation rates of the 20 kDa myosin light chains (MLC(20)), measured in aortic extracts, were nearly identical between WT and I-1((-/-)) mice. 4. In the portal vein, I-1 protein ablation was associated with a significant (P < 0.05) rightward shift in the EC(50) of isoproterenol relaxation (EC(50) = 10.4 +/- 1.4 nM) compared to the WT value (EC(50) = 3.5 +/- 0.2 nM). Contraction in response to acetylcholine as well as Ca(2+) sensitivity were similar between WT and I-1((-/-)) aorta. 5. Despite the prevalence of I-1 and its activation by PKA in the aorta, I-1 does not appear to play a significant role in contractile or relaxant responses to any pharmacomechanical or electromechanical agonists used. I-1 may play a role as a fine-tuning mechanism involved in regulating portal vein responsiveness to beta-adrenergic agonists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Essential role of rho kinase in the Ca2+ sensitization of prostaglandin F(2alpha)-induced contraction of rabbit aortae.J Physiol. 2003 Feb 1;546(Pt 3):823-36. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.030775. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12563007 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of CPI-17 and myosin phosphatase correlates with Ca(2+) sensitivity of protein kinase C-induced contraction in rabbit smooth muscle.J Physiol. 2001 Sep 1;535(Pt 2):553-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.t01-1-00553.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11533144 Free PMC article.
-
Redox signaling and splicing dependent change in myosin phosphatase underlie early versus late changes in NO vasodilator reserve in a mouse LPS model of sepsis.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015 May 1;308(9):H1039-50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00912.2014. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25724497 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic nucleotide-dependent relaxation pathways in vascular smooth muscle.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jan;69(2):247-66. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0815-2. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 21947498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of contractile activity in vascular smooth muscle by protein kinases.Rev Clin Basic Pharm. 1985 Jul-Dec;5(3-4):341-95. Rev Clin Basic Pharm. 1985. PMID: 3029813 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein phosphatase 1 inhibitor-1 deficiency reduces phosphorylation of renal NaCl cotransporter and causes arterial hypotension.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Mar;25(3):511-22. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012121202. Epub 2013 Nov 14. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24231659 Free PMC article.
-
Intra- and extrarenal arteries exhibit different profiles of contractile responses in high glucose conditions.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Dec;155(8):1204-13. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.365. Epub 2008 Sep 22. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18806819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alessi D, MacDougall LK, Sola MM, Ikebe M, Cohen P. The control of protein phosphatase-1 by targetting subunits. The major myosin phosphatase in avian smooth muscle is a novel form of protein phosphatase-1. European Journal of Biochemistry. 1992;210:1023–1035. - PubMed
-
- Allen PB, Hvalby O, Jensen V, Errington ML, Ramsay M, Chaudhry FA, Bliss TV, Storm-Mathisen J, Morris RG, Andersen P, Greengard P. Protein phosphatase-1 regulation in the induction of long-term potentiation: heterogeneous molecular mechanisms. Journal of Neuroscience. 2000;20:3537–3543. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatases. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1989;58:453–508. - PubMed
-
- Conti MA, Adelstein RS. The relationship between calmodulin binding and phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin kinase by the catalytic subunit of 3′:5′ cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1981;256:3178–3181. - PubMed
-
- de Lanerolle P, Paul RJ. Myosin phosphorylation/ dephosphorylation and regulation of airway smooth muscle contractility. American Journal of Physiology. 1991;261:L1–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 HL026057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 MH040899/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HL 52318/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 07382/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HL052318/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL026057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL054829/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 58429/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MH 40899/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HL 64018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DA 10044/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- HL 26057/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DA010044/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007382/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 59618/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P40 RR 12358/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064018/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL 64942/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059618/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL064942/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

