Selective activation of nociceptors by P2X receptor agonists in normal and inflamed rat skin
- PMID: 11454962
- PMCID: PMC2278707
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00437.x
Selective activation of nociceptors by P2X receptor agonists in normal and inflamed rat skin
Abstract
1. ATP can elicit pain in humans and, together with other P2X channel agonists, can produce nocifensive responses in rodents. We used the rat in vitro skin-nerve preparation to quantify primary afferent responses to ATP and its stable analogue alpha,beta-methylene ATP in normal and carrageenan-inflamed skin. 2. Both ATP and alpha,beta-methylene ATP were found to specifically activate the peripheral terminals of Adelta and C-fibre nociceptors in the skin. Thirty-nine per cent of the nociceptors tested responded to the maximal dose of alpha,beta-methylene ATP (5 mM). In contrast, non-nociceptive, low-threshold mechano-sensitive fibres were never activated by the same agonist concentrations. 3. Amongst the nociceptor population, C-mechanoheat fibres (C-MH or polymodal nociceptors) were markedly more responsive to P2X agonists than mechanonociceptors (C-M nociceptors) with Adelta- or C-fibre axons. Both C-mechanoheat and C-mechanonociceptors were activated by alpha,beta-methylene ATP doses as low as 50 microM. 4. In skin inflamed with carrageenan 3-4 h before recording both the number of responsive C-fibre nociceptors and their response magnitude increased. The increased neural response under inflammatory conditions was largely observed in C-mechanoheat or polymodal nociceptors. After low doses of P2X agonists C-MH fibres but not C-M fibres developed elevated ongoing activity and this effect was only seen after carrageenan inflammation. The time course of alpha,beta-methylene ATP-evoked discharges in nociceptors was found to correlate well with the time course of behavioural nocifensive responses in rats to the same agonist described in a previous study (Hamilton et al. 1999). 5. We conclude that the rapid increase in the number of alpha,beta-methylene ATP responsive nociceptors and the increased magnitude of the neural response following carrageenan inflammation explains why very low concentrations of such agonists can cause pain in inflammatory states.
Figures
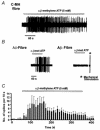
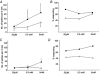

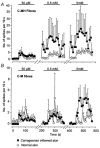

Similar articles
-
P2X purinoceptor-mediated excitation of trigeminal lingual nerve terminals in an in vitro intra-arterially perfused rat tongue preparation.J Physiol. 2000 May 1;524 Pt 3(Pt 3):891-902. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00891.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10790166 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for the involvement of endogenous ATP and P2X receptors in TMJ pain.Eur J Pain. 2005 Feb;9(1):87-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpain.2004.04.006. Eur J Pain. 2005. PMID: 15629879
-
Effects of spinally administered P2X receptor agonists and antagonists on the responses of dorsal horn neurones recorded in normal, carrageenan-inflamed and neuropathic rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Jan;129(2):351-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703047. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10694242 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of P2X3 homomeric and heteromeric channels to acute and chronic pain.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003 Aug;7(4):513-22. doi: 10.1517/14728222.7.4.513. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003. PMID: 12885270 Review.
-
P2X receptors mediate ATP-induced primary nociceptive neurone activation.J Auton Nerv Syst. 2000 Jul 3;81(1-3):146-51. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1838(00)00122-3. J Auton Nerv Syst. 2000. PMID: 10869713 Review.
Cited by
-
Ca2+ waves in keratinocytes are transmitted to sensory neurons: the involvement of extracellular ATP and P2Y2 receptor activation.Biochem J. 2004 Jun 1;380(Pt 2):329-38. doi: 10.1042/BJ20031089. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14967069 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 potentiation of P2X3 receptor mediated currents in dorsal root ganglion neurons.Mol Pain. 2007 Aug 10;3:22. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-3-22. Mol Pain. 2007. PMID: 17692121 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptive afferent activity alters the SI RA neuron response to mechanical skin stimulation.Cereb Cortex. 2010 Dec;20(12):2900-15. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhq039. Epub 2010 Mar 22. Cereb Cortex. 2010. PMID: 20308203 Free PMC article.
-
P2X purinoceptors and sensory transmission.Pflugers Arch. 2006 Aug;452(5):598-607. doi: 10.1007/s00424-006-0057-6. Epub 2006 Mar 18. Pflugers Arch. 2006. PMID: 16547751 Review.
-
Single-cell q-PCR derived expression profiles of identified sensory neurons.Mol Pain. 2019 Jan-Dec;15:1744806919884496. doi: 10.1177/1744806919884496. Mol Pain. 2019. PMID: 31588843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belyantseva IA, Lewin GR. Stability and plasticity of primary afferent projections following nerve regeneration and central degeneration. European Journal of Neuroscience. 1999;11:457–469. - PubMed
-
- Bleehen T, Keele CA. Observations on the algogenic actions of adenosine compounds on the human blister base preparation. Pain. 1977;3:367–377. - PubMed
-
- Bradbury EJ, Burnstock G, McMahon SB. The expression of P2X3 purinoreceptors in sensory neurons: effects of axotomy and glial-derived neurotrophic factor. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences. 1998;12:256–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

