Role of alpha(2)-adrenoceptors in the sympathetic inhibition of motility reflexes of guinea-pig ileum
- PMID: 11454964
- PMCID: PMC2278714
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00465.x
Role of alpha(2)-adrenoceptors in the sympathetic inhibition of motility reflexes of guinea-pig ileum
Abstract
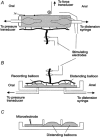
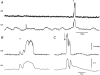
1. Sympathetic regulation of the motility of guinea-pig ileum was investigated using mesenteric nerve (MN) stimulation to inhibit motility reflexes, in vitro. 2. Transmural electrical stimulation (5 Hz, 1 s) in intact intestinal segments, or inflation of a balloon against the mucosa in opened segments, evoked contractions of the circular and longitudinal muscles oral to the stimulus. 3. MN stimulation (10 Hz, 5 s) usually abolished contractions of the longitudinal and circular muscles evoked by either electrical or mechanical stimuli. 4. The inhibition was mimicked by UK14,304 (70-100 nM) and abolished by idazoxan (100 nM), revealing an enhancement of circular muscle contractions. There was no evidence for alpha(2)-receptors on the muscle, suggesting sympathetic inhibition was via the myenteric plexus. 5. Possible sites of action of noradrenaline released from sympathetic nerves were investigated using intracellular recordings from the circular muscle in a multichambered organ bath. 6. When in the stimulation chamber, UK14,304 depressed (by 50 %) excitatory junction potentials (EJPs) recorded oral to a distension stimulus, but did not affect inhibitory junction potentials (IJPs) recorded anal to the stimulus. When added to a chamber between the stimulus and recording chambers, UK14,304 depressed EJPs by 40 %, but did not alter IJPs. When in the recording chamber, UK14,304 depressed EJPs by 20 %, but had no effect on IJPs. IJPs were inhibited, however, when UK14,304 was applied to the whole bath. 7. It is concluded that sympathetic activity inhibits intestinal motility mainly via alpha(2)-adrenoceptors on ascending interneurons and intrinsic sensory neurons of the orally directed reflex pathway.
Figures
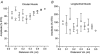
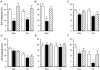
 , responses following washout. As for all subsequent column graphs, column heights represent mean response amplitudes while error bars indicate
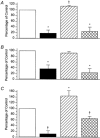
, responses following washout. As for all subsequent column graphs, column heights represent mean response amplitudes while error bars indicate 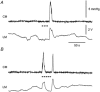
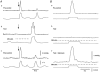
 , responses during MN stimulation in the presence of 100 n
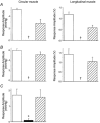
, responses during MN stimulation in the presence of 100 n , responses after washout during MN stimulation. A, circular muscle, intact tube preparation; B, longitudinal muscle, intact tube preparation; C, circular muscle, flattened preparation. In all cases, the inhibition of ascending contractions during MN stimulation was abolished by idazoxan. In addition, idazoxan revealed a significant facilitation by MN stimulation of circular muscle responses in both preparations. Symbols indicate significant differences from control, *P < 0.05; †P < 0.01; n = 5 in all cases.
, responses after washout during MN stimulation. A, circular muscle, intact tube preparation; B, longitudinal muscle, intact tube preparation; C, circular muscle, flattened preparation. In all cases, the inhibition of ascending contractions during MN stimulation was abolished by idazoxan. In addition, idazoxan revealed a significant facilitation by MN stimulation of circular muscle responses in both preparations. Symbols indicate significant differences from control, *P < 0.05; †P < 0.01; n = 5 in all cases.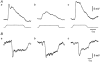
References
-
- Barthó L, Holzer P. Search for a physiological role of substance P in gastrointestinal motility. Neuroscience. 1985;16:1–32. - PubMed
-
- Barthó L, Maggi CA, Wilhelm M, Patacchini R. Tachykinin NK1 and NK2 receptors mediate atropine-resistant ileal circular muscle contractions evoked by capsaicin. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1994;259:187–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

