Adrenomedullin increases fluid extravasation from the splenic circulation of the rat
- PMID: 11454969
- PMCID: PMC2278709
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.00527.x
Adrenomedullin increases fluid extravasation from the splenic circulation of the rat
Abstract
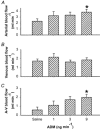
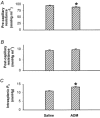
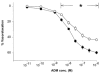
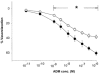
1. We studied the effect of adrenomedullin (ADM) on fluid efflux from the splenic vasculature into extravascular spaces. 2. Splenic arterial infusion of ADM (1, 3 and 9 ng min(-1); n = 9, 11 and 10, respectively) caused a dose-dependent increase in intrasplenic fluid efflux (+0.6 +/- 0.3 (saline) vs. +2.0 +/- 0.3 ml min(-1) (9 ng min(-1) ADM), P < 0.05), and in splenic (venous minus arterial) haematocrit (+0.8 +/- 0.1 (saline, n = 6) vs. +3.1 +/- 0.3 % (9 ng min(-1) ADM, n = 7), P < 0.05). There was no change in splenic weight (0.99 +/- 0.02 (saline, n = 6) vs. 0.99 +/- 0.02 g (9 ng min(-1) ADM, n = 7), P > 0.05). 3. There was no change in MAP before (97.5 +/- 2.2 mmHg), during (98.4 +/- 3.4 mmHg), or after (100.2 +/- 2.2 mmHg) intrasplenic infusion of ADM (9 ng min(-1)) (n = 11, P < 0.05). 4. ADM (9 ng min(-1)) caused an increase in intrasplenic microvascular pressure (11.3 +/- 0.3 (saline, n = 5) vs. 13.0 +/- 0.3 mmHg (9 ng min(-1) ADM, n = 6), P < 0.05). 5. ADM (1 x 10(-11) to 1 x 10(-6) M) induced greater vasorelaxation of isolated preconstricted splenic resistance arteries than veins (maximal relaxation: 60 +/- 0.9 (artery, n = 9) vs. 43 +/- 1.7 % (vein, n = 8), P < 0.05). L-NMMA (10(-4) M) partially inhibited the ADM-induced relaxation in splenic arteries (maximal relaxation: 38 +/- 3 (ADM + L-NMMA, n = 5) vs. 60 +/- 3 % (ADM + D-NMMA, n = 5), P < 0.05). 6. It is concluded that ADM increases fluid efflux from the splenic vasculature by differentially reducing pre- vs. post-capillary resistance, thus increasing intrasplenic microvascular pressure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nitric oxide increases fluid extravasation from the splenic circulation of the rat.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001 Apr;280(4):R959-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.2001.280.4.R959. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11247815
-
Atrial natriuretic factor increases splenic microvascular pressure and fluid extravasation in the rat.J Physiol. 2001 May 15;533(Pt 1):273-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0273b.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11351034 Free PMC article.
-
Splenic denervation worsens lipopolysaccharide-induced hypotension, hemoconcentration, and hypovolemia.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001 May;280(5):R1564-72. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.2001.280.5.R1564. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11294782
-
Potent and long-lasting vasodilatory effects of adrenomedullin in humans. Comparisons between normal subjects and patients with chronic heart failure.Circulation. 1997 Mar 4;95(5):1214-21. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.95.5.1214. Circulation. 1997. PMID: 9054852
-
Effect of portal hypertension on splenic blood flow, intrasplenic extravasation and systemic blood pressure.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003 Jun;284(6):R1580-5. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00516.2002. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12736184
Cited by
-
Adrenomedullin binding improves catecholamine responsiveness and kidney function in resuscitated murine septic shock.Intensive Care Med Exp. 2013 Dec;1(1):21. doi: 10.1186/2197-425X-1-2. Epub 2013 Oct 29. Intensive Care Med Exp. 2013. PMID: 26266790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrew PS, Deng Y, Sultanian R, Kaufman S. Nitric oxide increases fluid extravasation from the splenic circulation of the rat. American Journal of Physiology – Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 2001;280:R959–967. - PubMed
-
- Barman SA. Role of calcium-activated potassium channels and cyclic nucleotides on pulmonary vasoreactivity to serotonin. American Journal of Physiology. 1997;273:L142–147. - PubMed
-
- Cameron VA, Fleming AM. Novel sites of adrenomedullin gene expression in mouse and rat tissues. Endocrinology. 1998;139:2253–2264. - PubMed
-
- Ebara T, Miura K, Okumura M, Matsuura T, Kim S, Yukimura T, Iwao H. Effect of adrenomedullin on renal hemodynamics and functions in dogs. European Journal of Pharmacology. 1994;263:69–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

