A mechanism for increased contractile strength of human pennate muscle in response to strength training: changes in muscle architecture
- PMID: 11454977
- PMCID: PMC2278719
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.t01-1-00613.x
A mechanism for increased contractile strength of human pennate muscle in response to strength training: changes in muscle architecture
Abstract
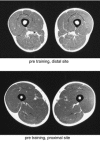
1. In human pennate muscle, changes in anatomical cross-sectional area (CSA) or volume caused by training or inactivity may not necessarily reflect the change in physiological CSA, and thereby in maximal contractile force, since a simultaneous change in muscle fibre pennation angle could also occur. 2. Eleven male subjects undertook 14 weeks of heavy-resistance strength training of the lower limb muscles. Before and after training anatomical CSA and volume of the human quadriceps femoris muscle were assessed by use of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), muscle fibre pennation angle (theta(p)) was measured in the vastus lateralis (VL) by use of ultrasonography, and muscle fibre CSA (CSA(fibre)) was obtained by needle biopsy sampling in VL. 3. Anatomical muscle CSA and volume increased with training from 77.5 +/- 3.0 to 85.0 +/- 2.7 cm(2) and 1676 +/- 63 to 1841 +/- 57 cm(3), respectively (+/- S.E.M.). Furthermore, VL pennation angle increased from 8.0 +/- 0.4 to 10.7 +/- 0.6 deg and CSA(fibre) increased from 3754 +/- 271 to 4238 +/- 202 microm (2). Isometric quadriceps strength increased from 282.6 +/- 11.7 to 327.0 +/- 12.4 N m. 4. A positive relationship was observed between theta(p) and quadriceps volume prior to training (r = 0.622). Multifactor regression analysis revealed a stronger relationship when theta(p) and CSA(fibre) were combined (R = 0.728). Post-training increases in CSA(fibre) were related to the increase in quadriceps volume (r = 0.749). 5. Myosin heavy chain (MHC) isoform distribution (type I and II) remained unaltered with training. 6. VL muscle fibre pennation angle was observed to increase in response to resistance training. This allowed single muscle fibre CSA and maximal contractile strength to increase more (+16 %) than anatomical muscle CSA and volume (+10 %). 7. Collectively, the present data suggest that the morphology, architecture and contractile capacity of human pennate muscle are interrelated, in vivo. This interaction seems to include the specific adaptation responses evoked by intensive resistance training.
Figures







References
-
- Aagaard P, Andersen JL. Correlation between contractile strength and myosin heavy chain isoform composition in human skeletal muscle. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. 1998;30:1217–1222. - PubMed
-
- Aagaard P, Andersen JL, Dyhre-Poulsen P, Leffers AM, Wagner, Aa, Magnusson SP, Halkjær-Kristensen J, Simonsen EB. The effect of resistance training on morphology and architecture of the human quadriceps muscle evaluated by MRI, ultrasound imaging and biopsy sampling. Journal of Physiology. 2000a;523.P:239P.
-
- Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Andersen JL, Magnusson SP, Halkjær-Kristensen J, Dyhre-Poulsen P. Neural inhibition during maximal eccentric and concentric quadriceps contraction: Effects of resistance training. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2000b;89:2249–2257. - PubMed
-
- Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Trolle M, Bangsbo J, Klausen K. Isokinetic hamstring/quadriceps strength ratio: influence from joint angular velocity, gravity correction and contraction mode. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. 1995;154:421–427. - PubMed
-
- Aagaard P, Simonsen EB, Trolle M, Bangsbo J, Klausen K. Specificity of training velocity and training load on gains in isokinetic knee joint strength. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica. 1996;156:123–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

