Evidence for a role of salicylic acid in the oxidative damage generated by NaCl and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis seedlings
- PMID: 11457953
- PMCID: PMC116459
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.126.3.1024
Evidence for a role of salicylic acid in the oxidative damage generated by NaCl and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis seedlings
Abstract
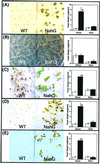
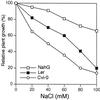
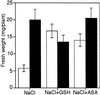
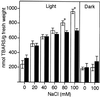
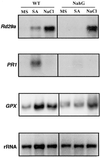
Previous studies have shown that salicylic acid (SA) is an essential component of the plant resistance to pathogens. We now show that SA plays a role in the plant response to adverse environmental conditions, such as salt and osmotic stresses. We have studied the responses of wild-type Arabidopsis and an SA-deficient transgenic line expressing a salicylate hydroxylase (NahG) gene to different abiotic stress conditions. Wild-type plants germinated under moderate light conditions in media supplemented with 100 mM NaCl or 270 mM mannitol showed extensive necrosis in the shoot. In contrast, NahG plants germinated under the same conditions remained green and developed true leaves. The lack of necrosis observed in NahG seedlings under the same conditions suggests that SA potentiates the generation of reactive oxygen species in photosynthetic tissues during salt and osmotic stresses. This hypothesis is supported by the following observations. First, the herbicide methyl viologen, a generator of superoxide radical during photosynthesis, produced a necrotic phenotype only in wild-type plants. Second, the presence of reactive oxygen-scavenging compounds in the germination media reversed the wild-type necrotic phenotype seen under salt and osmotic stress. Third, a greater increase in the oxidized state of the glutathione pool under NaCl stress was observed in wild-type seedlings compared with NahG seedlings. Fourth, greater oxidative damage occurred in wild-type seedlings compared with NahG seedlings under NaCl stress as measured by lipid peroxidation. Our data support a model for SA potentiating the stress response of the germinating Arabidopsis seedling.
Figures
References
-
- Botella MA, Quesada MA, Kononowicz A, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Valpuesta V. Characterization and in situ localization of a salt induced tomato peroxidase gene. Plant Mol Biol. 1994;25:105–114. - PubMed
-
- Boyer JS. Plant productivity and environment. Science. 1982;218:443–448. - PubMed
-
- Bray EA. Plant responses to water deficit. Trends Plant Sci. 1997;2:48–54.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

