Fatty acid synthesis in pea root plastids is inhibited by the action of long-chain acyl- coenzyme as on metabolite transporters
- PMID: 11457976
- PMCID: PMC116482
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.126.3.1259
Fatty acid synthesis in pea root plastids is inhibited by the action of long-chain acyl- coenzyme as on metabolite transporters
Abstract
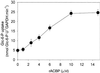
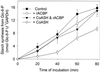
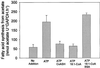
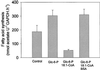
The uptake in vitro of glucose (Glc)-6-phosphate (Glc-6-P) into plastids from the roots of 10- to 14-d-old pea (Pisum sativum L. cv Puget) plants was inhibited by oleoyl-coenzyme A (CoA) concentrations in the low micromolar range (1--2 microM). The IC(50) (the concentration of inhibitor that reduces enzyme activity by 50%) for the inhibition of Glc-6-P uptake was approximately 750 nM; inhibition was reversed by recombinant rapeseed (Brassica napus) acyl-CoA binding protein. In the presence of ATP (3 mM) and CoASH (coenzyme A; 0.3 mM), Glc-6-P uptake was inhibited by 60%, due to long-chain acyl-CoA synthesis, presumably from endogenous sources of fatty acids present in the preparations. Addition of oleoyl-CoA (1 microM) decreased carbon flux from Glc-6-P into the synthesis of starch and through the oxidative pentose phosphate (OPP) pathway by up to 73% and 40%, respectively. The incorporation of carbon from Glc-6-P into fatty acids was not detected under any conditions. Oleoyl-CoA inhibited the incorporation of acetate into fatty acids by 67%, a decrease similar to that when ATP was excluded from incubations. The oleoyl-CoA-dependent inhibition of fatty acid synthesis was attributable to a direct inhibition of the adenine nucleotide translocator by oleoyl-CoA, which indirectly reduced fatty acid synthesis by ATP deprivation. The Glc-6-P-dependent stimulation of acetate incorporation into fatty acids was reversed by the addition of oleoyl-CoA.
Figures
References
-
- Barbier-Brygoo H, Joyard J, Pugin R. Intracellular compartmentation and plant cell signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 1997;2:214–222.
-
- Bowsher CG, Boulton EL, Rose J, Nayagam S, Emes MJ. Reductant for glutamate synthase is generated by the oxidative pentose-phosphate pathway in nonphotosynthetic root plastids. Plant J. 1993;2:893–898.
-
- Constantinides PP, Steim JM. Physical properties of fatty acyl-CoA: critical micelle concentrations and micellar size and shape. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:7573–7580. - PubMed
-
- Constantinides PP, Steim JM. Micellization of fatty acyl-CoA mixtures and its relevance to the fatty acyl selectivity of acyltransferases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988;261:430–436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

