Selective induction of E2F1 in response to DNA damage, mediated by ATM-dependent phosphorylation
- PMID: 11459832
- PMCID: PMC312742
Selective induction of E2F1 in response to DNA damage, mediated by ATM-dependent phosphorylation
Abstract
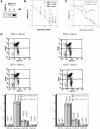
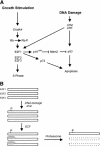
Previous work has established a role for p53 in triggering apoptosis in response to DNA damage; p53 also induces apoptosis in response to deregulation of the Rb cell cycle pathway. The latter event is consistent with a role for the Rb-regulated E2F1 protein as a specific inducer of apoptosis and p53 accumulation. We now show that DNA damage leads to a specific induction of E2F1 accumulation, dependent on ATM kinase activity and that the specificity of E2F1 induction reflects a specificity in the phosphorylation of E2F1 by ATM as well as the related kinase ATR. We identify a site for ATM/ATR phosphorylation in the amino terminus of E2F1 and we show that this site is required for ATM-mediated stabilization of E2F1. Finally, we also show that E2F1 is required for DNA damaged induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. We conclude that the cellular response to DNA damage makes use of signals from the Rb/E2F cell cycle pathway.
Figures

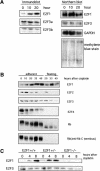


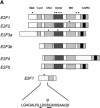

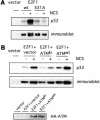
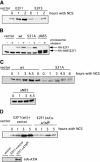
References
-
- Banin S, Moyal L, Shieh S, Taya Y, Anderson CW, Chessa L, Smorodinsky NI, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y, et al. Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science. 1998;281:1674–1677. - PubMed
-
- Bates S, Phillips AC, Clark PA, Stott F, Peters G, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH. p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature. 1998;395:124–125. - PubMed
-
- Canman CE, Lim DS, Cimprich KA, Taya Y, Tamai K, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Kastan MB, Siliciano JD. Activation of the ATM kinase by ionizing radiation and phosphorylation of p53. Science. 1998;281:1677–1679. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
