The set1Delta mutation unveils a novel signaling pathway relayed by the Rad53-dependent hyperphosphorylation of replication protein A that leads to transcriptional activation of repair genes
- PMID: 11459833
- PMCID: PMC312739
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.193901
The set1Delta mutation unveils a novel signaling pathway relayed by the Rad53-dependent hyperphosphorylation of replication protein A that leads to transcriptional activation of repair genes
Abstract
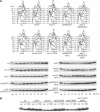
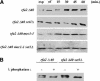
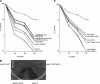
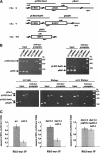
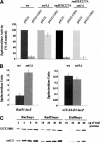
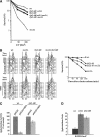
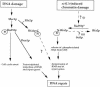
SET domain proteins are present in chromosomal proteins involved in epigenetic control of transcription. The yeast SET domain protein Set1p regulates chromatin structure, DNA repair, and telomeric functions. We investigated the mechanism by which the absence of Set1p increases DNA repair capacities of checkpoint mutants. We show that deletion of SET1 induces a response relayed by the signaling kinase Rad53p that leads to the MEC1/TEL1-independent hyperphosphorylation of replication protein A middle subunit (Rfa2p). Consequently, the binding of Rfa2p to upstream repressing sequences (URS) of repair genes is decreased, thereby leading to their derepression. Our results correlate the set1Delta-dependent phosphorylation of Rfa2p with the transcriptional induction of repair genes. Moreover, we show that the deletion of the amino-terminal region of Rfa2p suppresses the sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation of a mec3Delta checkpoint mutant, abolishes the URS-mediated repression, and increases the expression of repair genes. This work provides an additional link for the role of Rfa2p in the regulation of the repair capacity of the cell and reveals a role for the phosphorylation of Rfa2p and unveils unsuspected connections between chromatin, signaling pathways, telomeres, and DNA repair.
Figures
References
-
- Allen JB, Zhou Z, Siede W, Friedberg EC, Elledge SJ. The SAD1/RAD53 protein kinase controls multiple checkpoints and DNA damage-induced transcription in yeast. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:2416–2428. - PubMed
-
- Brill SJ, Stillman B. Replication factor-A from Saccharomyces cerevisiae is encoded by three essential genes coordinately expressed at S phase. Genes & Dev. 1991;5:1589–1600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
