Delivery of multiple epitopes by recombinant detoxified adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis induces protective antiviral immunity
- PMID: 11462005
- PMCID: PMC114968
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.16.7330-7338.2001
Delivery of multiple epitopes by recombinant detoxified adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis induces protective antiviral immunity
Abstract
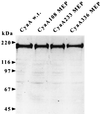
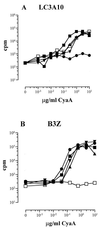
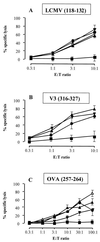
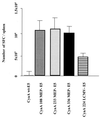
CyaA, the adenylate cyclase toxin from Bordetella pertussis, can deliver its N-terminal catalytic domain into the cytosol of a large number of eukaryotic cells and particularly into professional antigen-presenting cells. We have previously identified within the primary structure of CyaA several permissive sites at which insertion of peptides does not alter the ability of the toxin to enter cells. This property has been exploited to design recombinant CyaA toxoids capable of delivering major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-restricted CD8(+) T-cell epitopes into antigen-presenting cells and to induce specific CD8(+) cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) responses in vivo. Here we have explored the capacity of the CyaA vector carrying several different CD8(+) T-cell epitopes to prime multiple CTL responses. The model vaccine consisted of a polyepitope made of three CTL epitopes from lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV), the V3 region of human immunodeficiency virus gp120, and chicken ovalbumin, inserted at three different sites of the catalytic domain of genetically detoxified CyaA. Each of these epitopes was processed on delivery by CyaA and presented in vitro to specific T-cell hybridomas. Immunization of mice by CyaA toxoids carrying the polyepitope lead to the induction of specific CTL responses for each of the three epitopes, as well as to protection against a lethal viral challenge. Moreover, mice primed against the vector by mock CyaA or a recombinant toxoid were still able to develop strong CTL responses after subsequent immunization with a recombinant CyaA carrying a foreign CD8(+) CTL epitope. These results highlight the potency of the adenylate cyclase vector for induction of protective CTL responses with multiple specificity and/or broad MHC restriction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo induction of CTL responses by recombinant adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis carrying viral CD8+ T cell epitopes.J Immunol. 1996 Jun 15;156(12):4697-706. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8648115
-
Therapy of murine tumors with recombinant Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase carrying a cytotoxic T cell epitope.J Immunol. 1999 Apr 1;162(7):4157-62. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10201941
-
Induction of a polarized Th1 response by insertion of multiple copies of a viral T-cell epitope into adenylate cyclase of Bordetella pertussis.Infect Immun. 2000 Jul;68(7):3867-72. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.7.3867-3872.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10858196 Free PMC article.
-
The adenylate cyclase toxin from Bordetella pertussis--a novel promising vehicle for antigen delivery to dendritic cells.Int J Med Microbiol. 2004 Apr;293(7-8):571-6. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00291. Int J Med Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15149033 Review.
-
Adenylate cyclase toxin-hemolysin relevance for pertussis vaccines.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014 Oct;13(10):1215-27. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2014.944900. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2014. PMID: 25090574 Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition of mycobacterial antigens delivered by genetically detoxified Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase by T cells from cattle with bovine tuberculosis.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6255-61. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6255-6261.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501751 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of epitope prediction and molecular docking allows for good identification of MHC class I restricted T-cell epitopes.Comput Biol Chem. 2013 Aug;45:30-5. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2013.03.003. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Comput Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23666426 Free PMC article.
-
Nanobody-Antigen Conjugates Elicit HPV-Specific Antitumor Immune Responses.Cancer Immunol Res. 2018 Jul;6(7):870-880. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0661. Epub 2018 May 23. Cancer Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29792298 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of a MalE CD4(+)-T-cell epitope into the major histocompatibility complex class II antigen presentation pathway by Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase.Infect Immun. 2002 Feb;70(2):1002-5. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.1002-1005.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11796640 Free PMC article.
-
A highly optimized DNA vaccine confers complete protective immunity against high-dose lethal lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus challenge.Vaccine. 2011 Sep 9;29(39):6755-62. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.12.064. Epub 2011 Jan 14. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21238574 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

