Human herpesvirus 8 envelope glycoprotein K8.1A interaction with the target cells involves heparan sulfate
- PMID: 11462024
- PMCID: PMC114987
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.16.7517-7527.2001
Human herpesvirus 8 envelope glycoprotein K8.1A interaction with the target cells involves heparan sulfate
Abstract
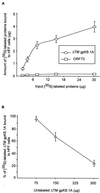
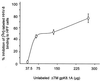
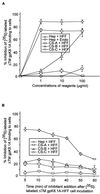
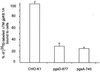
Human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8) or Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K8.1 gene encodes for two immunogenic glycoproteins, gpK8.1A and gpK8.1B, originating from spliced messages. The 228-amino-acid (aa) gpK8.1A is the predominant form associated with the virion envelope, consisting of a 167-aa region identical to gpK8.1B and a 61-aa unique region (L. Zhu, V. Puri, and B. Chandran, Virology 262:237-249, 1999). HHV-8 has a broad in vivo and in vitro cellular tropism, and our studies showed that this may be in part due to HHV-8's interaction with the ubiquitous host cell surface molecule, heparan sulfate (HS). Since HHV-8 K8.1 gene is positionally colinear to the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gene encoding the gp350/gp220 protein involved in EBV binding to the target cells, gpK8.1A's ability to interact with the target cells was examined. The gpK8.1A without the transmembrane and carboxyl domains (DeltaTMgpK8.1A) was expressed in a baculovirus system and purified. Radiolabeled purified DeltaTMgpK8.1A protein bound to the target cells, which was blocked by unlabeled DeltaTMgpK8.1A. Unlabeled DeltaTMgpK8.1A blocked the binding of [(3)H]thymidine-labeled purified HHV-8 to the target cells. Binding of radiolabeled DeltaTMgpK8.1A to the target cells was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner by soluble heparin, a glycosaminoglycan (GAG) closely related to HS, but not by other GAGs such as chondroitin sulfate A and C, N-acetyl heparin and de-N-sulfated heparin. Cell surface absorbed DeltaTMgpK8.1A was displaced by soluble heparin. Radiolabeled DeltaTMgpK8.1A also bound to HS expressing Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells, and binding to mutant CHO cell lines deficient in HS was significantly reduced. The DeltaTMgpK8.1A specifically bound to heparin-agarose beads, which was inhibited by HS and heparin, but not by other GAGs. Virion envelope-associated gpK8.1A was specifically precipitated by heparin-agarose beads. These findings suggest that gpK8.1A interaction with target cells involves cell surface HS-like moieties, and HHV-8 interaction with HS could be in part mediated by virion envelope-associated gpK8.1A.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human herpesvirus 8 envelope-associated glycoprotein B interacts with heparan sulfate-like moieties.Virology. 2001 Jun 5;284(2):235-49. doi: 10.1006/viro.2001.0921. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11384223
-
Human herpesvirus 8 envelope glycoprotein B mediates cell adhesion via its RGD sequence.J Virol. 2003 Mar;77(5):3131-47. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.5.3131-3147.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12584338 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesvirus 8 interaction with target cells involves heparan sulfate.Virology. 2001 Apr 10;282(2):245-55. doi: 10.1006/viro.2000.0851. Virology. 2001. PMID: 11289807
-
The role of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the virus replication cycle.Acta Virol. 1998 Apr;42(2):103-18. Acta Virol. 1998. PMID: 9770079 Review.
-
Heparan sulfate: anchor for viral intruders?Biochimie. 2001 Aug;83(8):811-7. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(01)01290-1. Biochimie. 2001. PMID: 11530214 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of entry and infection of monocytic THP-1 cells by Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus (KSHV): role of heparan sulfate, DC-SIGN, integrins and signaling.Virology. 2010 Oct 10;406(1):103-16. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.07.012. Epub 2010 Aug 1. Virology. 2010. PMID: 20674951 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonism of host antiviral responses by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus tegument protein ORF45.PLoS One. 2010 May 11;5(5):e10573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010573. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20485504 Free PMC article.
-
The murine gammaherpesvirus-68 gp150 acts as an immunogenic decoy to limit virion neutralization.PLoS One. 2007 Aug 8;2(8):e705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000705. PLoS One. 2007. PMID: 17684552 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Heparan Sulfate in Herpesvirus Infection.Virol Sin. 2008 Dec 1;23(6):383-393. doi: 10.1007/s12250-008-2992-1. Virol Sin. 2008. PMID: 19956628 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus virions inhibit interferon responses induced by envelope glycoprotein gpK8.1.J Virol. 2006 Nov;80(22):11105-14. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00846-06. Epub 2006 Sep 6. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16956942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akula S M, Wang F-Z, Vierira J, Chandran B. Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8/KSHV) infection of target cells involves interaction with heparan sulfate. Virology. 2001;282:245–255. - PubMed
-
- Ballestas M E, Chatis P A, Kaye K M. Efficient persistence of extrachromosomal KSHV DNA mediated by latency-associated nuclear antigen. Science. 1999;284:641–644. - PubMed
-
- Boshoff C, Schulz T F, Kennedy M M, Graham A K, Fisher C, Thomas A, McGee J O, Weiss R A, O'Leary J J. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infects endothelial and spindle cells. Nat Med. 1995;1:1274–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

