Reactivation of latent human cytomegalovirus in CD14(+) monocytes is differentiation dependent
- PMID: 11462026
- PMCID: PMC114989
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.16.7543-7554.2001
Reactivation of latent human cytomegalovirus in CD14(+) monocytes is differentiation dependent
Abstract
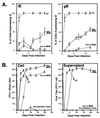
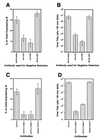
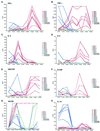
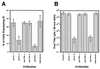
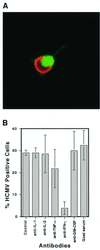
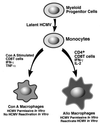
We have previously demonstrated reactivation of latent human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) in myeloid lineage cells obtained from healthy donors. Virus was obtained from allogenically stimulated monocyte-derived macrophages (Allo-MDM), but not from macrophages differentiated by mitogenic stimulation (ConA-MDM). In the present study, the cellular and cytokine components essential for HCMV replication and reactivation were examined in Allo-MDM. The importance of both CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells in the generation of HCMV-permissive Allo-MDM was demonstrated by negative selection or blocking experiments using antibodies directed against both HLA class I and HLA class II molecules. Interestingly, contact of monocytes with CD4 or CD8 T cells was not essential for reactivation of HCMV, since virus was observed in macrophages derived from CD14(+) monocytes stimulated by supernatants produced by allogeneic stimulation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Examination of the cytokines produced in Allo-MDM and ConA-MDM cultures indicated a significant difference in the kinetics of production and quantity of these factors. Further examination of the cytokines essential for the generation of HCMV-permissive Allo-MDM identified gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) but not interleukin-1 or -2, tumor necrosis factor alpha, or granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor as critical components in the generation of these macrophages. In addition, although IFN-gamma was crucial for reactivation of latent HCMV, addition of IFN-gamma to unstimulated macrophage cultures was insufficient to reactivate virus. Thus, this study characterizes two distinct monocyte-derived cell types which can be distinguished by their ability to reactivate and support HCMV replication and identifies the critical importance of IFN-gamma in the reactivation of HCMV.
Figures


References
-
- Bostrom L, Ringden O, Jacobsen N, Zwaan F, Nilsson B. A European multicenter study of chronic graft-versus-host disease: the role of cytomegalovirus serology in recipients and donors-acute graft-versus-host disease, and splenectomy. Transplantation. 1990;49:1100–1105. - PubMed
-
- Bowden R A. Transfusion-transmitted cytomegalovirus infection. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1995;9:155–166. - PubMed
-
- Burns G, Begley C, Mackay I, Triglia R, Werkmeister J. Supernatural killer cells. Immunol Today. 1985;6:370–373. - PubMed
-
- Chou S, Kim D Y, Norman D J. Transmission of cytomegalovirus by pretransplant leukocyte transfusions in renal transplant candidates. J Infect Dis. 1987;155:565–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

