Degradation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor by the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein is important for functional inactivation and is separable from proteasomal degradation of E7
- PMID: 11462030
- PMCID: PMC114993
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.16.7583-7591.2001
Degradation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor by the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein is important for functional inactivation and is separable from proteasomal degradation of E7
Abstract
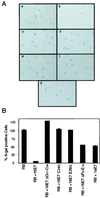
The steady-state level and metabolic half-life of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein pRB are decreased in cells that express high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) E7 proteins. Here we show that pRB degradation is a direct activity of E7 and does not reflect a property of cell lines acquired during the selection process for E7 expression. An amino-terminal domain of E7 that does not directly contribute to pRB binding but is required for transformation is also necessary for E7-mediated pRB degradation. Treatment with inhibitors of the 26S proteasome not only blocks E7-mediated pRB degradation but also causes the stabilization of E7. Mutagenic analyses, however, reveal that the processes of proteasomal degradation of E7 and pRB are not linked processes. HPV type 16 E7 also targets the pRB-related proteins p107 and p130 for destabilization by a proteasome-dependent mechanism. Using the SAOS2 flat-cell assay as a biological indicator for pRB function, we demonstrate that pRB degradation, not solely binding, is important for the E7-induced inactivation of pRB.
Figures




References
-
- Alunni-Fabbroni M, Littlewood T, Deleu L, Caldeira S, Giarre M, Dell' Orco M, Tommasino M. Induction of S phase and apoptosis by the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein are separable events in immortalized rodent fibroblasts. Oncogene. 2000;19:2277–2285. - PubMed
-
- An B, Dou Q P. Cleavage of retinoblastoma protein during apoptosis: an interleukin 1 beta-converting enzyme-like protease as candidate. Cancer Res. 1996;56:438–442. - PubMed
-
- Baker S J, Markowitz S, Fearon E R, Willson J K V, Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990;249:912–915. - PubMed
-
- Banks L, Edmonds C, Vousden K. Ability of the HPV16 E7 protein to bind RB and induce DNA synthesis is not sufficient for efficient transforming activity in NIH 3T3 cells. Oncogene. 1990;5:1383–1389. - PubMed
-
- Berezutskaya E, Bagchi S. The human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein functionally interacts with the S4 subunit of the 26S proteasome. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:30135–30140. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

