Enhancement of muscle gene delivery with pseudotyped adeno-associated virus type 5 correlates with myoblast differentiation
- PMID: 11462038
- PMCID: PMC115001
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.16.7662-7671.2001
Enhancement of muscle gene delivery with pseudotyped adeno-associated virus type 5 correlates with myoblast differentiation
Abstract
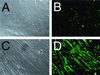
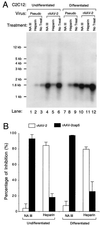
Adeno-associated virus (AAV)-based muscle gene therapy has achieved tremendous success in numerous animal models of human diseases. Recent clinical trials with this vector have also demonstrated great promise. However, to achieve therapeutic benefit in patients, large inocula of virus will likely be necessary to establish the required level of transgene expression. For these reasons, efforts aimed at increasing the efficacy of AAV-mediated gene delivery to muscle have the potential for improving the safety and therapeutic benefit in clinical trials. In the present study, we compared the efficiency of gene delivery to mouse muscle cells for recombinant AAV type 2 (rAAV-2) and rAAV-2cap5 (AAV-2 genomes pseudo-packaged into AAV-5 capsids). Despite similar levels of transduction by these two vectors in undifferentiated myoblasts, pseudotyped rAAV-2cap5 demonstrated dramatically enhanced transduction in differentiated myocytes in vitro (>500-fold) and in skeletal muscle in vivo (>200-fold) compared to rAAV-2. Serotype-specific differences in transduction efficiency did not directly correlate with viral binding to muscle cells but rather appeared to involve endocytic or intracellular barriers to infection. Furthermore, application of this pseudotyped virus in a mouse model of Duchenne's muscular dystrophy also demonstrated significantly improved transduction efficiency. These findings should have a significant impact on improving rAAV-mediated gene therapy in muscle.
Figures


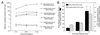





References
-
- Chao H, Liu Y, Rabinowitz J, Li C, Samulski R J, Walsh C E. Several log increase in therapeutic transgene delivery by distinct adeno-associated viral serotype vectors. Mol Ther. 2000;2:619–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

