Viral load increases in SJL/J mice persistently infected by Theiler's virus after inactivation of the beta(2)m gene
- PMID: 11462045
- PMCID: PMC115008
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.16.7723-7726.2001
Viral load increases in SJL/J mice persistently infected by Theiler's virus after inactivation of the beta(2)m gene
Abstract
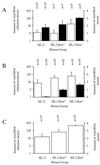
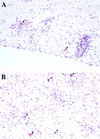
We show that inactivating the beta(2)m gene increases the viral load of SJL/J mice persistently infected by Theiler's virus. Together with previous results, this shows that the characteristics of Tmevp1, a locus which controls the amount of viral RNA that persists in the central nervous system, are those of an H-2 class I gene.
Figures
References
-
- Aubert C, Chamorro M, Brahic M. Identification of Theiler's virus infected cells in the central nervous system of the mouse during demyelinating disease. Microb Pathog. 1987;3:319–326. - PubMed
-
- Azoulay-Cayla A, Syan S, Brahic M, Bureau J F. Roles of the H-2Db and H-2Kb genes in resistance to persistent Theiler's murine encephalomyelitis virus infection of the central nervous system. J Gen Virol. 2001;82:1043–1047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

