Monoclonal antibodies that bind to domain III of dengue virus E glycoprotein are the most efficient blockers of virus adsorption to Vero cells
- PMID: 11462053
- PMCID: PMC115016
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.16.7769-7773.2001
Monoclonal antibodies that bind to domain III of dengue virus E glycoprotein are the most efficient blockers of virus adsorption to Vero cells
Abstract
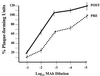
The specific mechanisms by which antibodies neutralize flavivirus infectivity are not completely understood. To study these mechanisms in more detail, we analyzed the ability of a well-defined set of anti-dengue (DEN) virus E-glycoprotein-specific monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) to block virus adsorption to Vero cells. In contrast to previous studies, the binding sites of these MAbs were localized to one of three structural domains (I, II, and III) in the E glycoprotein. The results indicate that most MAbs that neutralize virus infectivity do so, at least in part, by the blocking of virus adsorption. However, MAbs specific for domain III were the strongest blockers of virus adsorption. These results extend our understanding of the structure-function relationships in the E glycoprotein of DEN virus and provide the first direct evidence that domain III encodes the primary flavivirus receptor-binding motif.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson R, King A D, Innis B L. Correlation of E protein binding with cell susceptibility to dengue 4 virus infection. J Gen Virol. 1992;73:2155–2159. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Maguire T, Hileman R E, Fromm J R, Esko J D, Linhardt R J, Marks R M. Dengue virus infectivity depends on envelope protein binding to target cell heparan sulfate. Nat Med. 1997;3:866–871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

