Role for p53 in gene induction by double-stranded RNA
- PMID: 11462054
- PMCID: PMC115017
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.16.7774-7777.2001
Role for p53 in gene induction by double-stranded RNA
Abstract
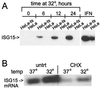
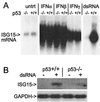
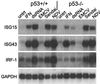
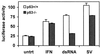
Cross talk between p53 and interferon-regulated pathways is implicated in the induction of gene expression by biologic and genotoxic stresses. We demonstrate that the interferon-stimulated gene ISG15 is induced by p53 and that p53 is required for optimal gene induction by double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), but not interferon. Interestingly, virus induces ISG15 in the absence of p53, suggesting that virus and dsRNA employ distinct signaling pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Double-stranded RNA induces iNOS gene expression in Schwann cells, sensory neuronal death, and peripheral nerve demyelination.Glia. 2007 May;55(7):712-22. doi: 10.1002/glia.20493. Glia. 2007. PMID: 17348024
-
Signal regulatory protein alpha negatively regulates both TLR3 and cytoplasmic pathways in type I interferon induction.Mol Immunol. 2008 Jun;45(11):3025-35. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.03.012. Epub 2008 May 8. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18471880
-
Transcriptional signaling by double-stranded RNA: role of TLR3.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005 Feb;16(1):1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2005.01.006. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005. PMID: 15733829 Review.
-
Double-stranded RNA stimulates chemokine expression in microglia through vacuolar pH-dependent activation of intracellular signaling pathways.J Neurochem. 2005 Oct;95(1):273-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03354.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 16181431
-
Mechanisms of induction and action of interferons.Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2009;71(1-2):51-71. Verh K Acad Geneeskd Belg. 2009. PMID: 19739398 Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor Suppressor p53 Inhibits Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Downregulating HBx via E6AP-Mediated Proteasomal Degradation in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Lines.Viruses. 2022 Oct 21;14(10):2313. doi: 10.3390/v14102313. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36298868 Free PMC article.
-
Control of signaling-mediated clearance of apoptotic cells by the tumor suppressor p53.Science. 2015 Jul 31;349(6247):1261669. doi: 10.1126/science.1261669. Science. 2015. PMID: 26228159 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological rescue of mutant p53 triggers spontaneous tumor regression via immune responses.Cell Rep Med. 2025 Mar 18;6(3):101976. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.101976. Epub 2025 Feb 21. Cell Rep Med. 2025. PMID: 39986271 Free PMC article.
-
Translating p53-based therapies for cancer into the clinic.Nat Rev Cancer. 2024 Mar;24(3):192-215. doi: 10.1038/s41568-023-00658-3. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38287107 Review.
-
ISG15 and ISGylation in Human Diseases.Cells. 2022 Feb 4;11(3):538. doi: 10.3390/cells11030538. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159348 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amundson S A, Myers T G, Fornace A J., Jr Roles for p53 in growth arrest and apoptosis: putting on the brakes after genotoxic stress. Oncogene. 1998;17:3287–3299. - PubMed
-
- Baker S J, Markowitz S, Fearon E R, Willson J K, Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990;249:912–915. - PubMed
-
- Bandyopadhyay S K, Leonard G T, Jr, Bandyopadhyay T, Stark G R, Sen G C. Transcriptional induction by double-stranded RNA is mediated by interferon-stimulated response elements without activation of interferon-stimulated gene factor 3. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:19624–19629. - PubMed
-
- Blomstrom D C, Fahey D, Kutny R, Korant B D, Knight E., Jr Molecular characterization of the interferon-induced 15-kDa protein. Molecular cloning and nucleotide and amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1986;261:8811–8816. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

