Disruption of gamma-glutamyl leukotrienase results in disruption of leukotriene D(4) synthesis in vivo and attenuation of the acute inflammatory response
- PMID: 11463821
- PMCID: PMC87261
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.16.5389-5395.2001
Disruption of gamma-glutamyl leukotrienase results in disruption of leukotriene D(4) synthesis in vivo and attenuation of the acute inflammatory response
Abstract
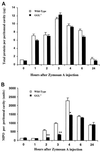
To study the function of gamma-glutamyl leukotrienase (GGL), a newly identified member of the gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) family, we generated null mutations in GGL (GGL(tm1)) and in both GGL and GGT (GGL(tm1)-GGT(tm1)) by a serial targeting strategy using embryonic stem cells. Mice homozygous for GGL(tm1) show no obvious phenotypic changes. Mice deficient in both GGT and GGL have a phenotype similar to the GGT-deficient mice, but approximately 70% of these mice die before 4 weeks of age, at least 2 months earlier than mice deficient only in GGT. These double-mutant mice are unable to cleave leukotriene C(4) (LTC(4)) to LTD(4), indicating that this conversion is completely dependent on the two enzymes, and in some organs (spleen and uterus) deletion of GGL alone abolished more than 90% of this activity. In an experimental model of peritonitis, GGL alone is responsible for the generation of peritoneal LTD(4). Further, during the development of peritonitis, GGL-deficient mice show an attenuation in neutrophil recruitment but not of plasma protein influx. These findings demonstrate an important role for GGL in the inflammatory response and suggest that LTC(4) and LTD(4) have distinctly different functions in the inflammatory process.
Figures



References
-
- Bradley P P, Priebat D A, Christensen R D, Rothstein G. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Investig Dermatol. 1982;78:206–209. - PubMed
-
- Buckner C K, Krell R D, Laravuso R B, Coursin D B, Bernstein P R, Will J A. Pharmacological evidence that human intralobar airways do not contain different receptors that mediate contractions to leukotriene C4 and leukotriene D4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986;237:558–562. - PubMed
-
- Byrum R S, Goulet J L, Snouwaert J N, Griffiths R J, Koller B H. Determination of the contribution of cysteinyl leukotrienes and leukotriene B4 in acute inflammatory responses using 5-lipoxygenase- and leukotriene A4 hydrolase-deficient mice. J Immunol. 1999;163:6810–6819. - PubMed
-
- Carter B Z, Wiseman A L, Orkiszewski R, Ballard K D, Ou C N, Lieberman M W. Metabolism of leukotriene C4 in γ-glutamyl transpeptidase-deficient mice. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:12305–12310. - PubMed
-
- Carter B Z, Shi Z Z, Barrios R, Lieberman M W. γ-Glutamyl leukotrienase, a γ-glutamyl transpeptidase gene family member, is expressed primarily in spleen. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:28277–28285. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
