Paralytic zebrafish lacking acetylcholine receptors fail to localize rapsyn clusters to the synapse
- PMID: 11466415
- PMCID: PMC6762670
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05439.2001
Paralytic zebrafish lacking acetylcholine receptors fail to localize rapsyn clusters to the synapse
Abstract
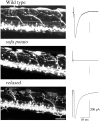
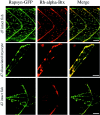
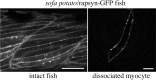
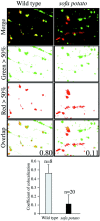
Physiological analysis of two lines of paralytic mutant zebrafish, relaxed and sofa potato, reveals defects in distinct types of receptors in skeletal muscle. In sofa potato the paralysis results from failed synaptic transmission because of the absence of acetylcholine receptors, whereas relaxed mutants lack dihydropyridine receptor-mediated release of internal calcium in response to the muscle action potential. Synaptic structure and function appear normal in relaxed, showing that muscle paralysis per se does not impede proper synapse development. However, sofa potato mutants show incomplete development of the postsynaptic complex. Specifically, in the absence of ACh receptors, clusters of the receptor-aggregating protein rapsyn form in the extrasynaptic membrane but generally fail to localize to the subsynaptic region. Our results indicate that, although rapsyn molecules are capable of self-aggregation, interaction with ACh receptors is required for proper subsynaptic localization.
Figures




References
-
- Adams BA, Tanabe T, Mikami A, Numa S, Beam KG. Intramembrane charge movement restored in dysgenic skeletal muscle by injection of dihydropyridine receptor cDNAs. Nature. 1990;346:569–572. - PubMed
-
- Apel ED, Roberds SL, Campbell KP, Merlie JP. Rapsyn may function as a link between the acetylcholine receptor and the agrin-binding dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex. Neuron. 1995;15:15–26. - PubMed
-
- Apel ED, Glass DJ, Moscoso LM, Yancopoulos GD, Sanes JR. Rapsyn is required for MuSK signaling and recruits synaptic components to a MuSK-containing scaffold. Neuron. 1997;18:623–635. - PubMed
-
- Burden SJ. The formation of neuromuscular synapses. Genes Dev. 1998;12:133–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
