The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is involved in associative learning in rabbits
- PMID: 11466422
- PMCID: PMC6762655
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05513.2001
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase is involved in associative learning in rabbits
Abstract
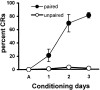
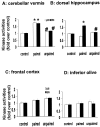
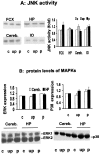
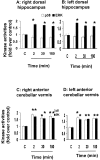
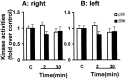
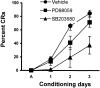
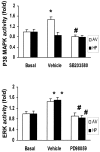
This study examined the role of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family during acquisition of the rabbit's classically conditioned eye-blink response. Eye-blink conditioning produced a significant, bilateral activation of both extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERKs) and p38 MAPK in the anterior cerebellar vermis. There was also a significant bilateral activation of ERKs in the dorsal hippocampus with no change in p38 MAPK. These changes were seen at 2 min after the last conditioning session, were maintained for at least 180 min, and occurred without any change in the protein expression of either ERKs or p38 MAPK. There were no changes in ERKs or p38 MAPK in frontal cortex, in cerebellar hemispheral lobule VI, or in a section of brainstem containing the inferior olive. Moreover, the stress-related protein kinase Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), another subfamily of MAPKs, was not altered in any of the brain regions examined. Animals receiving explicitly unpaired presentations of a conditioned stimulus and an unconditioned stimulus did not acquire conditioned responses (CRs) and did not demonstrate any changes in ERKs, p38 MAPK, or JNK. The intraventricular injection of SB203580, a selective p38 MAPK inhibitor, significantly retarded CR acquisition and blocked the learning-related increases in p38 MAPK activity in the anterior vermis. PD98059, a selective MAPK kinase inhibitor, had a smaller and only marginally significant effect on CR acquisition, although it did block the learning-related increases in ERK activity in both the hippocampus and anterior vermis. These results indicate that p38 MAPK is activated during associative learning and may play a role in the transcriptional events that lead to memory consolidation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stimulation of MAPK cascades by insulin and osmotic shock: lack of an involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in glucose transport in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Diabetes. 2000 Nov;49(11):1783-93. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.11.1783. Diabetes. 2000. PMID: 11078444
-
Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades during priming of human neutrophils by TNF-alpha and GM-CSF.J Leukoc Biol. 1998 Oct;64(4):537-45. J Leukoc Biol. 1998. PMID: 9766635
-
Regulation of p42/p44 MAPK and p38 MAPK by the adenosine A(1) receptor in DDT(1)MF-2 cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2001 Feb 16;413(2-3):151-61. doi: 10.1016/s0014-2999(01)00761-0. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11226388
-
The neuronal MAP kinase cascade: a biochemical signal integration system subserving synaptic plasticity and memory.J Neurochem. 2001 Jan;76(1):1-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00054.x. J Neurochem. 2001. PMID: 11145972 Review.
-
A patent review of MAPK inhibitors (2018 - present).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2023 Jan-Jun;33(6):421-444. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2023.2242584. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2023. PMID: 37501497 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of the serotonin 5-HT(2A) receptor in learning.Learn Mem. 2003 Sep-Oct;10(5):355-62. doi: 10.1101/lm.60803. Learn Mem. 2003. PMID: 14557608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NMDA and dopamine converge on the NMDA-receptor to induce ERK activation and synaptic depression in mature hippocampus.PLoS One. 2006 Dec 27;1(1):e138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000138. PLoS One. 2006. PMID: 17205142 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal c-Jun-N-terminal kinases serve as negative regulators of associative learning.J Neurosci. 2010 Oct 6;30(40):13348-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3492-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20926661 Free PMC article.
-
Memory-specific temporal profiles of gene expression in the hippocampus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Dec 10;99(25):16279-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.242597199. Epub 2002 Dec 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. PMID: 12461180 Free PMC article.
-
p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates myelination.J Mol Neurosci. 2008 May;35(1):23-33. doi: 10.1007/s12031-007-9011-0. Epub 2007 Nov 10. J Mol Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 17994198 Review.
References
-
- Aloyo VJ, Romano AG, Harvey JA. Evidence for an involvement of the mu-type of opioid receptor in the modulation of learning. Neuroscience. 1993;55:511–519. - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Bailey CH, Kaang BK, Chen M, Martin KC, Lim CS, Casadio A, Kandel ER. Mutation in the phosphorylation sites of MAP kinase blocks learning-related internalization of apCAM in Aplysia sensory neurons. Neuron. 1997;18:913–924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
