Activation of expressed KCNQ potassium currents and native neuronal M-type potassium currents by the anti-convulsant drug retigabine
- PMID: 11466425
- PMCID: PMC6762632
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-15-05535.2001
Activation of expressed KCNQ potassium currents and native neuronal M-type potassium currents by the anti-convulsant drug retigabine
Abstract
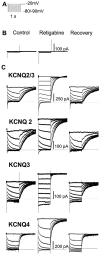
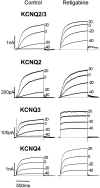
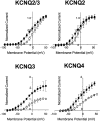
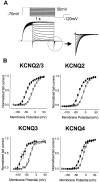
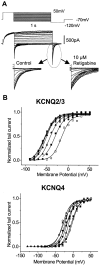
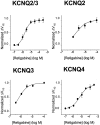
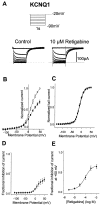
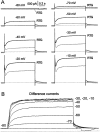
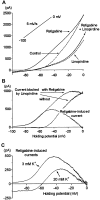
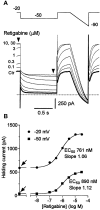
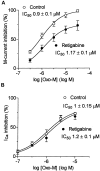
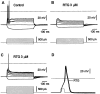
Retigabine [D-23129; N-(2-amino-4-(4-fluorobenzylamino)-phenyl) carbamic acid ethyl ester] is a novel anticonvulsant compound that is now in clinical phase II development. It has previously been shown to enhance currents generated by KCNQ2/3 K(+) channels when expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells (Main et al., 2000; Wickenden et al., 2000). In the present study, we have compared the actions of retigabine on KCNQ2/3 currents with those on currents generated by other members of the KCNQ family (homomeric KCNQ1, KCNQ2, KCNQ3, and KCNQ4 channels) expressed in CHO cells and on the native M current in rat sympathetic neurons [thought to be generated by KCNQ2/3 channels (Wang et al., 1998)]. Retigabine produced a hyperpolarizing shift of the activation curves for KCNQ2/3, KCNQ2, KCNQ3, and KCNQ4 currents with differential potencies in the following order: KCNQ3 > KCNQ2/3 > KCNQ2 > KCNQ4, as measured either by the maximum hyperpolarizing shift in the activation curves or by the EC(50) values. In contrast, retigabine did not enhance cardiac KCNQ1 currents. Retigabine also produced a hyperpolarizing shift in the activation curve for native M channels in rat sympathetic neurons. The retigabine-induced current was inhibited by muscarinic receptor stimulation, with similar agonist potency but 25% reduced maximum effect. In unclamped neurons, retigabine produced a hyperpolarization and reduced the number of action potentials produced by depolarizing current injections, without change in action potential configuration.
Figures

References
-
- Barhanin J, Lesage F, Guillemare E, Fink M, Lazdunski M, Romey G. KvLQT1 and lsK (minK) proteins associate to form the IKs cardiac potassium current. Nature. 1996;384:78–80. - PubMed
-
- Biervert C, Schroeder BC, Kubisch C, Berkovic SF, Propping P, Jentsch T, Steinlein OK. A potassium channel mutation in neonatal human epilepsy. Science. 1998;279:403–406. - PubMed
-
- Brown DA. M-currents. In: Narahashi T, editor. Ion channels, Vol 1. Plenum; New York: 1988. pp. 55–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
