Mystery solved: discovery of a novel integrin ligand in the developing kidney
- PMID: 11470814
- PMCID: PMC2150774
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200106124
Mystery solved: discovery of a novel integrin ligand in the developing kidney
Abstract
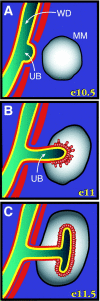
Mutant mice lacking the integrin alpha8 subunit exhibit variable defects in kidney development with most mutants missing both kidneys. Several lines of evidence indicate that the known extracellular matrix ligands for integrin alpha8beta1 are either dispensable for or not involved in alpha8beta1 signaling during kidney development. This suggests the presence of an unknown ligand. A novel alpha8beta1 ligand, nephronectin, has now been identified. Nephronectin is a new extracellular matrix protein associated with the Wolffian duct and the ureteric bud, epithelial structures with well-defined roles in kidney development.
Figures
Comment on
-
Identification and characterization of a novel extracellular matrix protein nephronectin that is associated with integrin alpha8beta1 in the embryonic kidney.J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 23;154(2):447-58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200103069. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11470831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brandenberger, R., A. Schmidt, J. Linton, D. Wang, C. Backus, S. Denda, U. Muller, and L.F. Reichardt. 2001. Identification and characterization of a novel extracellular matrix protein nephronectin that is associated with integrin α8β1 in the embryonic kidney. J. Cell Biol. 154:447–458. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Glassock, R.J., and S.G. Massry. 2001. Other congenital disorders. Massry and Glassock's Textbook of Nephrology. S.G. Massry and R.J. Glassock, editors. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA. 865–868.

