Novel p62dok family members, dok-4 and dok-5, are substrates of the c-Ret receptor tyrosine kinase and mediate neuronal differentiation
- PMID: 11470823
- PMCID: PMC2150770
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200102032
Novel p62dok family members, dok-4 and dok-5, are substrates of the c-Ret receptor tyrosine kinase and mediate neuronal differentiation
Abstract
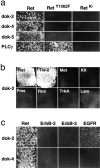
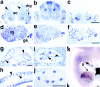
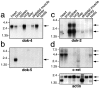
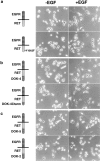
Docking proteins are substrates of tyrosine kinases and function in the recruitment and assembly of specific signal transduction molecules. Here we found that p62dok family members act as substrates for the c-Ret receptor tyrosine kinase. In addition to dok-1, dok-2, and dok-3, we identified two new family members, dok-4 and dok-5, that can directly associate with Y1062 of c-Ret. Dok-4 and dok-5 constitute a subgroup of dok family members that is coexpressed with c-Ret in various neuronal tissues. Activated c-Ret promotes neurite outgrowth of PC12 cells; for this activity, Y1062 in c-Ret is essential. c-Ret/dok fusion proteins, in which Y1062 of c-Ret is deleted and replaced by the sequences of dok-4 or dok-5, induce ligand-dependent axonal outgrowth of PC12 cells, whereas a c-Ret fusion containing dok-2 sequences does not elicit this response. Dok-4 and dok-5 do not associate with rasGAP or Nck, in contrast to p62dok and dok-2. Moreover, dok-4 and dok-5 enhance c-Ret-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Thus, we have identified a subclass of p62dok proteins that are putative links with downstream effectors of c-Ret in neuronal differentiation.
Figures









References
-
- Alberti, L., M.G. Borrello, S. Ghizzoni, F. Torriti, M.G. Rizzetti, and M.A. Pierotti. 1998. Grb2 binding to the different isoforms of Ret tyrosine kinase. Oncogene. 17:1079–1087. - PubMed
-
- Arighi, E., L. Alberti, F. Torriti, S. Ghizzoni, M.G. Rizzetti, G. Pelicci, B. Pasini, I. Bongarzone, C. Piutti, M.A. Pierotti, and M.G. Borrello. 1997. Identification of Shc docking site on Ret tyrosine kinase. Oncogene. 14:773–782. - PubMed
-
- Asai, N., H. Murakami, T. Iwashita, and M. Takahashi. 1996. A mutation at tyrosine 1062 in MEN2A-Ret and MEN2B-Ret impairs their transforming activity and association with shc adaptor proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 271:17644–17649. - PubMed
-
- Avantaggiato, V., N.A. Dathan, M. Grieco, N. Fabien, D. Lazzaro, A. Fusco, A. Simeone, and M. Santoro. 1994. Developmental expression of the RET protooncogene. Cell Growth Differ. 5:305–311. - PubMed
-
- Behrens, J., J.P. von Kries, M. Kuhl, L. Bruhn, D. Wedlich, R. Grosschedl, and W. Birchmeier. 1996. Functional interaction of β-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature. 382:638–642. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

