Molecular evolution of the homeodomain family of transcription factors
- PMID: 11470884
- PMCID: PMC55828
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.15.3258
Molecular evolution of the homeodomain family of transcription factors
Abstract
The homeodomain family of transcription factors plays a fundamental role in a diverse set of functions that include body plan specification, pattern formation and cell fate determination during metazoan development. Members of this family are characterized by a helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motif known as the homeodomain. Homeodomain proteins regulate various cellular processes by specifically binding to the transcriptional control region of a target gene. These proteins have been conserved across a diverse range of species, from yeast to human. A number of inherited human disorders are caused by mutations in homeodomain-containing proteins. In this study, we present an evolutionary classification of 129 human homeodomain proteins. Phylogenetic analysis of these proteins, whose sequences were aligned based on the three-dimensional structure of the homeodomain, was performed using a distance matrix approach. The homeodomain proteins segregate into six distinct classes, and this classification is consistent with the known functional and structural characteristics of these proteins. An ancestral sequence signature that accurately describes the unique sequence characteristics of each of these classes has been derived. The phylogenetic analysis, coupled with the chromosomal localization of these genes, provides powerful clues as to how each of these classes arose from the ancestral homeodomain.
Figures
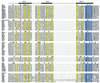
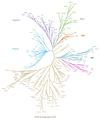

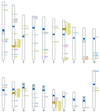
References
-
- McGinnis W., Levine,M.S., Hafen,E., Kuroiwa,A. and Gehring,W.J. (1984) A conserved DNA sequence in homoeotic genes of the Drosophila Antennapedia and bithorax complexes. Nature, 308, 428–433. - PubMed
-
- Gehring W.J., Affolter,M. and Burglin,T. (1994) Homeodomain proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem., 63, 487–526. - PubMed
-
- Dekker N., Cox,M., Boelens,R., Verrijzer,C., van der Vliet,P. and Kaptein,R. (1993) Solution structure of the POU-specific DNA-binding domain of Oct-1. Nature, 362, 852–855. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

