Enhanced expression and production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in myocarditis
- PMID: 11472393
- PMCID: PMC1906075
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01510.x
Enhanced expression and production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in myocarditis
Abstract
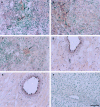
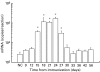
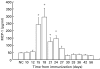
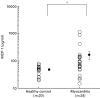
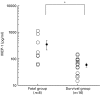
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) is a member of the C-C chemokine family that has been shown to play a major role in the migration of monocytes and T cells to an inflammatory focus. To clarify the role of MCP-1 in the pathogenesis of myocarditis, we have examined the expression of MCP-1 in rat hearts with experimental autoimmune myocarditis (EAM), and have also measured serum levels of MCP-1 in patients with histology-proven acute myocarditis. Lewis rats were immunized with cardiac myosin and were killed 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 42 and 56 days after immunization. Large mononuclear cells in the myocardial interstitium were stained with an anti-MCP-1 antibody. mRNA of MCP-1 increased in the hearts of EAM rats from days 15--27 as shown by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Serum MCP-1 levels of the rats with EAM were significantly elevated from days 15--24. In the clinical study, serum levels of MCP-1 in 24 patients with acute myocarditis at the time of admission (165.2 +/- 55.8 pg/ml) were significantly (P = 0.0301) elevated compared with those of 20 healthy volunteers (61.8 +/- 10.7 pg/ml). Serum MCP-1 levels of 8 fatal cases (371.8 +/- 145.2 pg/ml) were significantly (P = 0.0058) higher than those of 16 cases who survived (65.5 +/- 12.8 pg/ml). In conclusions, MCP-1 may play an important role in the pathogenesis of human acute myocarditis as well as in the progression of rat EAM.
Figures
References
-
- Rollins BJ. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1: a potential regulator of monocyte recruitment in inflammatory disease. Mol Med Today. 1996;2:198–204. - PubMed
-
- Adams DH, Lloyd AR. Chemokines: leukocyte recruitment and activation cytokines. Lancet. 1997;349:490–5. - PubMed
-
- Shyy Y-J, Li Y-S, Kolattukudy PE. Activation of MCP-1 gene expression is mediated through multiple signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;192:693–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

