Novel immunosuppressive effect of FK506 by augmentation of T cell apoptosis
- PMID: 11472421
- PMCID: PMC1906112
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01586.x
Novel immunosuppressive effect of FK506 by augmentation of T cell apoptosis
Abstract
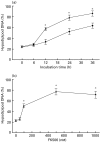
We have recently reported the accumulation of oligoclonal activated T cells in the spontaneously developed autoimmune pancreatitis in aly/aly mouse. In this study, we examined the effects of FK506 in this mouse model in preventing autoimmune pancreatitis and investigated its action on calcium signalling apoptosis of alymphoplasia (aly) lymphocytes in vitro. Mice were treated with FK506 from 8 to 25 weeks of age. At the age of 15 weeks, minimal mononuclear cell infiltration was observed in the pancreas in both the FK506 treated group and the control group. Furthermore, a marked cell infiltration associated with destruction of acini and partial fatty changes were observed in 25-week-old control mice. In contrast, FK506 treated mice showed almost no tissue destruction or mononuclear cell infiltration at the age of 25 weeks. Furthermore, at 15 weeks of age, most mononuclear cells in FK506-treated mice were TUNEL positive, whereas only a few were positive in control mice. This augmentation of T cell apoptosis by FK506 was confirmed using naive splenocytes activated by PMA and ionomycin in vitro. Finally, a suppressive effect of FK506 on Bcl-2 production but not on Bax production was confirmed by Western blotting. This unique effect of FK506 on the augmentation of T cell apoptosis is probably one of the mechanisms explaining its beneficial effect on aly autoimmune pancreatitis.
Figures



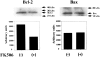
References
-
- Ellis RE, Yuan JY, Horvitz HR. Mechanism and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–98. - PubMed
-
- Smith CA, Williams GT, Kingston RE, Jenkinson J, Owen JJT. Antibodies to CD3/T-cell receptor complex induce cell death by apoptosis in immature T cells in thymic culture. Nature (Lond) 1989;337:181–4. - PubMed
-
- Ucker DS, Ashwell JD, Nichas G. Activation-driven T cell death: requirement for de novo transactivation and translation and association with genome fragmentation. J Immunol. 1989;143:3461–9. - PubMed
-
- Choi DW. Excitotoxic cell death. J Neurobiol. 1992;23:1261–76. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

