Differentiation of Lactobacillus plantarum, L. pentosus, and L. paraplantarum by recA gene sequence analysis and multiplex PCR assay with recA gene-derived primers
- PMID: 11472918
- PMCID: PMC93042
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.8.3450-3454.2001
Differentiation of Lactobacillus plantarum, L. pentosus, and L. paraplantarum by recA gene sequence analysis and multiplex PCR assay with recA gene-derived primers
Abstract
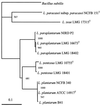
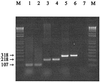
In this study, we succeeded in differentiating Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus pentosus, and Lactobacillus paraplantarum by means of recA gene sequence comparison. Short homologous regions of about 360 bp were amplified by PCR with degenerate consensus primers, sequenced, and analyzed, and 322 bp were considered for the inference of phylogenetic trees. Phylograms, obtained by parsimony, maximum likelihood, and analysis of data matrices with the neighbor-joining model, were coherent and clearly separated the three species. The validity of the recA gene and RecA protein as phylogenetic markers is discussed. Based on the same sequences, species-specific primers were designed, and a multiplex PCR protocol for the simultaneous distinction of these bacteria was optimized. The sizes of the amplicons were 318 bp for L. plantarum, 218 bp for L. pentosus, and 107 bp for L. paraplantarum. This strategy permitted the unambiguous identification of strains belonging to L. plantarum, L. pentosus, and L. paraplantarum in a single reaction, indicating its applicability to the speciation of isolates of the L. plantarum group.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of recA gene sequence analysis in the identification and discrimination of Lactobacillus hilgardii strains isolated from stuck wine fermentations.Int J Food Microbiol. 2007 Apr 1;115(1):70-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2006.10.032. Epub 2006 Dec 14. Int J Food Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17174001
-
Genotypic diversity of stress response in Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus paraplantarum and Lactobacillus pentosus.Int J Food Microbiol. 2012 Jul 2;157(2):278-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2012.05.018. Epub 2012 May 25. Int J Food Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22704047
-
Rapid differentiation and in situ detection of 16 sourdough lactobacillus species by multiplex PCR.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Jun;71(6):3049-59. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.6.3049-3059.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15933001 Free PMC article.
-
Intraspecies discrimination of Lactobacillus paraplantarum by PCR.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2011 Mar;316(1):70-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2010.02193.x. Epub 2011 Jan 24. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2011. PMID: 21204929
-
Characterization of Lactobacillus isolates from fermented olives and their bacteriocin gene profiles.Food Microbiol. 2011 Dec;28(8):1514-8. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2011.07.010. Epub 2011 Aug 3. Food Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21925038
Cited by
-
Natural Lactic Acid Bacteria Population and Silage Fermentation of Whole-crop Wheat.Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2015 Aug;28(8):1123-32. doi: 10.5713/ajas.14.0955. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci. 2015. PMID: 26104520 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and in vitro assessment of potential probiotic characteristics and antibacterial effects of Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum SKI19, a bacteriocinogenic strain isolated from Thai fermented pork sausage.J Food Sci Technol. 2018 Jul;55(7):2774-2785. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3201-3. Epub 2018 Jun 6. J Food Sci Technol. 2018. PMID: 30042594 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Comparative Analysis of Lactiplantibacillus pentosus Isolates Autochthonous to Cucumber Fermentation Reveals Subclades of Divergent Ancestry.Foods. 2023 Jun 23;12(13):2455. doi: 10.3390/foods12132455. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37444193 Free PMC article.
-
Technological Parameters, Anti-Listeria Activity, Biogenic Amines Formation and Degradation Ability of L. plantarum Strains Isolated from Sheep-Fermented Sausage.Microorganisms. 2021 Sep 7;9(9):1895. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9091895. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34576790 Free PMC article.
-
Strain diversity of plant-associated Lactiplantibacillus plantarum.Microb Biotechnol. 2021 Sep;14(5):1990-2008. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13871. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Microb Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34171185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bergey D H, Harrison F C, Breed R S, Hammer B W, Huntoon F M. Lactobacillus plantarum, In: Buchanan R E, Gibbons N E, editors. Bergey's manual of determinative bacteriology. 1st ed. Baltimore, Md: The Williams & Wilkins Co.; 1923. p. 250.
-
- Berthier F, Ehrlich S D. Rapid species identification within two groups of closely related lactobacilli using PCR primers that target the 16S/23S rRNA spacer region. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1998;161:97–106. - PubMed
-
- Bringel F, Curk M-C, Hubert J-C. Characterization of lactobacilli by Southern-type hybridization with a Lactobacillus plantarum pyrDFE probe. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1996;46:588–594. - PubMed
-
- Collins M D, Rodrigues U M, Ash C, Aguirre M, Farrow J A E, Martinez-Murcia A, Phillips B A, Williams A M, Wallbanks S. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Lactobacillus and related lactic acid bacteria as determined by reverse transcriptase sequencing of 16S rRNA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991;77:5–12.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

