Characterization and analysis of a stable serotype-associated membrane protein (P30) of Mycoplasma agalactiae
- PMID: 11473997
- PMCID: PMC88244
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.8.2814-2822.2001
Characterization and analysis of a stable serotype-associated membrane protein (P30) of Mycoplasma agalactiae
Abstract
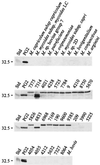
The gene for a 30-kDa immunodominant antigen, P30, of Mycoplasma agalactiae was cloned from type strain PG2 and expressed in Escherichia coli. P30 is encoded on a monocistronic operon determined by two -10 boxes and a possible -35 region constituting the potential promoter, and a transcription termination site. The gene for the 266-amino-acid protein is preceded by a polypurine-rich region designed as the consensus sequence for a ribosome-binding site. Analysis of the amino acid sequence of P30 revealed the presence of a recognition site for a prokaryotic signal peptidase II at amino acid (aa) 24, indicating that P30 is a transmembrane protein. Moreover, Triton X-114 phase partitioning of M. agalactiae PG2 total antigen revealed that P30 is strongly hydrophobic and hence a possible membrane component. Immunoblot analysis using the monospecific polyclonal anti-P30-His serum indicated that P30 is specific to M. agalactiae. Furthermore, PCR amplification with specific primers for p30 and Southern blot analysis revealed the presence of the gene in all M. agalactiae strains tested and its absence in the other mycoplasma species. Among 27 strains of M. agalactiae studied, 20 strains belonging to the common serotypes A to D, including PG2, expressed P30 or part of it as detected by the monospecific polyclonal anti-P30 antibodies. The other seven strains belonging to the rarely isolated serotypes E to H were negative for P30. The p30 gene was sequenced in 15 strains of M. agalactiae, 10 of which expressed P30 or at least part of it and 5 of which did not express P30. The negative strains carried mutations in both -10 boxes of the promoters. These mutations seem to be responsible for the lack of P30 expression in these strains. Analysis of sera from sheep that were experimentally infected with M. agalactiae revealed that P30 induced a strong and persistent immune response which was still very high two months after infection. In contrast, currently used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay serology gave only low titers.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of P40, a cytadhesin of Mycoplasma agalactiae.Infect Immun. 2002 Oct;70(10):5612-21. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.10.5612-5621.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12228289 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Recombinant P48 of Mycoplasma agalactiae by Site Directed Mutagenesis and its Immunological Characterization.Anim Biotechnol. 2017 Jan 2;28(1):11-17. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2016.1189926. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Anim Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 27385225
-
Species identification of Mycoplasma bovis and Mycoplasma agalactiae based on the uvrC genes by PCR.Mol Cell Probes. 1998 Jun;12(3):161-9. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.1998.0160. Mol Cell Probes. 1998. PMID: 9664578
-
[Molecular basis of Mycoplasma agalactiae pathogenicity].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004 Nov-Dec;117(11-12):472-9. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004. PMID: 15584429 Review. German.
-
Alternative inhibitors of mycoplasma adherence.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1996;408:107-11. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-0415-9_12. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1996. PMID: 8895782 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Host cell interactions of novel antigenic membrane proteins of Mycoplasma agalactiae.BMC Microbiol. 2022 Apr 8;22(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12866-022-02512-2. BMC Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35395771 Free PMC article.
-
A novel chimeric recombinant protein PDHB-P80 of Mycoplasma agalactiae as a potential diagnostic tool.Mol Biol Res Commun. 2020 Sep;9(3):123-128. doi: 10.22099/mbrc.2020.37684.1513. Mol Biol Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 33313332 Free PMC article.
-
Mycoplasma agalactiae Vaccines: Current Status, Hurdles, and Opportunities Due to Advances in Pathogenicity Studies.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Feb 2;12(2):156. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12020156. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38400139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a sensitive and specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on recombinant antigens for rapid detection of antibodies against Mycoplasma agalactiae in sheep.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Apr;14(4):420-5. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00439-06. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17287317 Free PMC article.
-
The liposoluble proteome of Mycoplasma agalactiae: an insight into the minimal protein complement of a bacterial membrane.BMC Microbiol. 2010 Aug 25;10:225. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-225. BMC Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20738845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K, editors. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1999.
-
- Bergonier D, DeSimone F, Russo P, Solsona M, Lambert M, Poumarat F. Variable expression and geographic distribution of Mycoplasma agalactiae surface epitopes demonstrated with monoclonal antibodies. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1996;143:159–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

