Quantitation of varicella-zoster virus DNA in patients with Ramsay Hunt syndrome and zoster sine herpete
- PMID: 11474003
- PMCID: PMC88250
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.8.2856-2859.2001
Quantitation of varicella-zoster virus DNA in patients with Ramsay Hunt syndrome and zoster sine herpete
Abstract
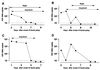
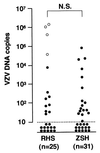
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) reactivation causes facial nerve palsy in Ramsay Hunt syndrome (RHS) and zoster sine herpete (ZSH) with and without zoster rash, respectively. In the present study, we analyzed the VZV DNA copy number in saliva samples from 25 patients with RHS and 31 patients with ZSH using a TaqMan PCR assay to determine differences in the viral load between the two diseases. VZV copy number in saliva peaked near the day of the appearance of zoster in patients with RHS. Consequently, VZV DNA was less frequently detected in patients with RHS who exhibited facial palsy several days after the appearance of zoster. These findings suggest that the VZV load in saliva samples reflects the kinetics of viral reactivation in patients with RHS. In addition, VZV DNA was equally detected in saliva from patients with RHS and ZSH, and there was no significant difference in the highest viral copy number between patients with RHS and those with ZSH. The VZV load does not appear to reflect a major difference between RHS and ZSH.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of varicella-zoster virus DNA in peripheral mononuclear cells from patients with Ramsay Hunt syndrome or zoster sine herpete.J Med Virol. 1998 Dec;56(4):359-63. J Med Virol. 1998. PMID: 9829642
-
Varicella-zoster virus DNA level and facial paralysis in Ramsay Hunt syndrome.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2004 Sep;113(9):700-5. doi: 10.1177/000348940411300905. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2004. PMID: 15453526
-
Reactivation of varicella-zoster virus in delayed facial palsy after dental treatment and oro-facial surgery.J Med Virol. 2000 Sep;62(1):42-5. J Med Virol. 2000. PMID: 10935987
-
Varicella-zoster virus and virus DNA in the blood and oropharynx of people with latent or active varicella-zoster virus infections.J Clin Virol. 2014 Dec;61(4):487-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2014.09.012. Epub 2014 Oct 2. J Clin Virol. 2014. PMID: 25453570 Review.
-
Neurological disease produced by varicella zoster virus reactivation without rash.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;342:243-53. doi: 10.1007/82_2009_3. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20186614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Search for varicella zoster virus DNA in saliva of healthy individuals aged 20-59 years.J Med Virol. 2014 Feb;86(2):360-2. doi: 10.1002/jmv.23834. Epub 2013 Nov 6. J Med Virol. 2014. PMID: 24338812 Free PMC article.
-
Varicella zoster virus in Bell's palsy: a prospective study.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2010 May-Jun;76(3):370-3. doi: 10.1590/S1808-86942010000300016. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2010. PMID: 20658018 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial and viral pathogens in saliva: disease relationship and infectious risk.Periodontol 2000. 2011 Feb;55(1):48-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2010.00361.x. Periodontol 2000. 2011. PMID: 21134228 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
A Case Report: PCR-Assisted Diagnosis of Varicella in an Adult.Open J Med Microbiol. 2012 Sep;2(3):10.4236/ojmm.2012.23019. doi: 10.4236/ojmm.2012.23019. Open J Med Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 24409401 Free PMC article.
-
Ramsay Hunt syndrome with multiple cranial neuropathy: a literature review.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022 May;279(5):2239-2244. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-07136-2. Epub 2021 Oct 23. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 34687339 Review.
References
-
- Davison A J, Scott J E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986;67:1759–1816. - PubMed
-
- Furuta Y, Takasu T, Sato K C, Fukuda S, Inuyama Y, Hondo R, Nagashima K. Detection of varicella-zoster virus DNA in human geniculate ganglia by polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:1157–1159. - PubMed
-
- Furuta Y, Fukuda S, Suzuki S, Takasu T, Inuyama Y, Nagashima K. Detection of varicella-zoster virus DNA in patients with acute peripheral facial palsy by the polymerase chain reaction, and its use for early diagnosis of zoster sine herpete. J Med Virol. 1997;52:316–319. - PubMed
-
- Furuta Y, Ohtani F, Kawabata H, Fukuda S, Bergström T. High prevalence of varicella-zoster virus reactivation in herpes simplex virus-seronegative patients with acute peripheral facial palsy. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;30:529–533. - PubMed
-
- Furuta Y, Ohtani F, Mesuda Y, Fukuda S, Inuyama Y. Early diagnosis of zoster sine herpete and antiviral therapy for the treatment of facial palsy. Neurology. 2000;55:708–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

