The relative roles of passive surface forces and active ion transport in the modulation of airway surface liquid volume and composition
- PMID: 11479349
- PMCID: PMC2233832
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.118.2.223
The relative roles of passive surface forces and active ion transport in the modulation of airway surface liquid volume and composition
Abstract
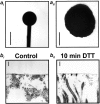
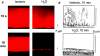
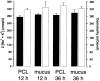
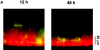
Two hypotheses have been proposed recently that offer different views on the role of airway surface liquid (ASL) in lung defense. The "compositional" hypothesis predicts that ASL [NaCl] is kept low (<50 mM) by passive forces to permit antimicrobial factors to act as a chemical defense. The "volume" hypothesis predicts that ASL volume (height) is regulated isotonically by active ion transport to maintain efficient mechanical mucus clearance as the primary form of lung defense. To compare these hypotheses, we searched for roles for: (1) passive forces (surface tension, ciliary tip capillarity, Donnan, and nonionic osmolytes) in the regulation of ASL composition; and (2) active ion transport in ASL volume regulation. In primary human tracheobronchial cultures, we found no evidence that a low [NaCl] ASL could be produced by passive forces, or that nonionic osmolytes contributed substantially to ASL osmolality. Instead, we found that active ion transport regulated ASL volume (height), and that feedback existed between the ASL and airway epithelia to govern the rate of ion transport and volume absorption. The mucus layer acted as a "reservoir" to buffer periciliary liquid layer height (7 microm) at a level optimal for mucus transport by donating or accepting liquid to or from the periciliary liquid layer, respectively. These data favor the active ion transport/volume model hypothesis to describe ASL physiology.
Figures








References
-
- Bansil R., Stanley E., LaMont J.T. Mucin biophysics. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1995;57:635–657. - PubMed
-
- Davril M., Degroote S., Humbert P., Galabert C., Dumur V., Lafitte J.J., Lamblin G., Roussel P. The sialylation of bronchial mucins secreted by patients suffering from cystic fibrosis or from chronic bronchitis is related to the severity of airway infection. Glycobiology. 1999;9:311–321. - PubMed
-
- Goldman M.J., Anderson G.M., Stolzenberg E.D., Kari U.P., Zasloff M., Wilson J.M. Human beta-defensin-1 is a salt-sensitive antibiotic that is inactivated in cystic fibrosis. Cell. 1997;88:553–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

